
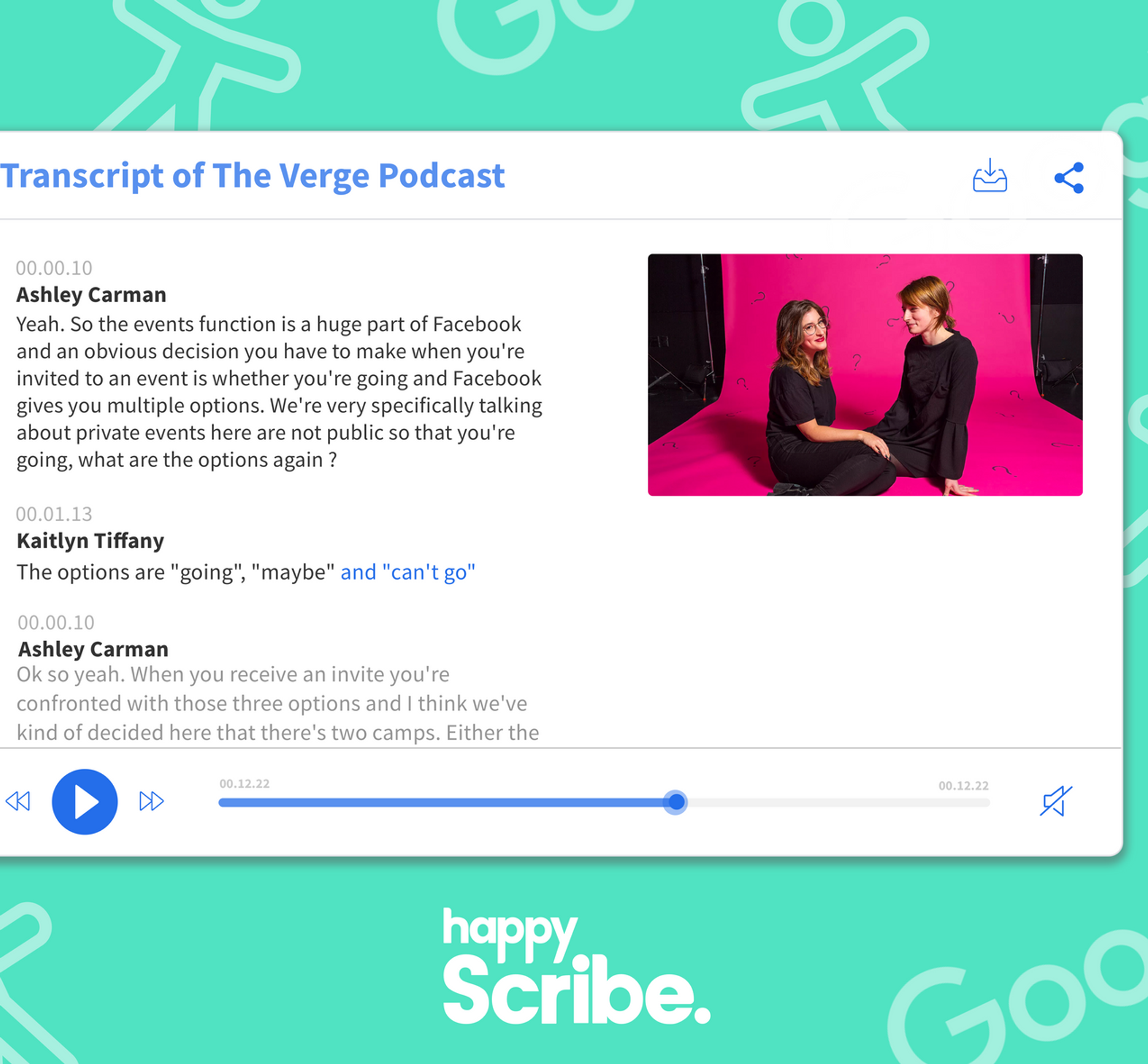
What Turnaround Time Should You Expect From a Transcription Service?
From AI drafts to human review, this guide breaks down real transcription services' turnaround times, costs, and risks. Make the right choice today.

From AI drafts to human review, this guide breaks down real transcription services' turnaround times, costs, and risks. Make the right choice today.

Looking for a better AI note taker? Compare the top 5 tl;dv alternatives for 2026. Find the right fit for global teams, sales workflows, and privacy

Struggling to download a YouTube transcript? Compare free methods, tools, and when HappyScribe is the better choice for accurate, reusable text.

Looking for a European AI note taker? We tested GDPR-compliant tools with EU hosting, strong accuracy, and real-world workflows.

Compare the best AI note takers for journalists in 2026. See which tools work best for interviews, accuracy, security, and workflows.

Turn talk into action. Discover the best meeting agenda apps for 2026 that combine smart planning, AI recording, and automated task tracking.

Learn how to write an objective summary with AI, plus examples, best practices, and tools to keep summaries factual and unbiased.

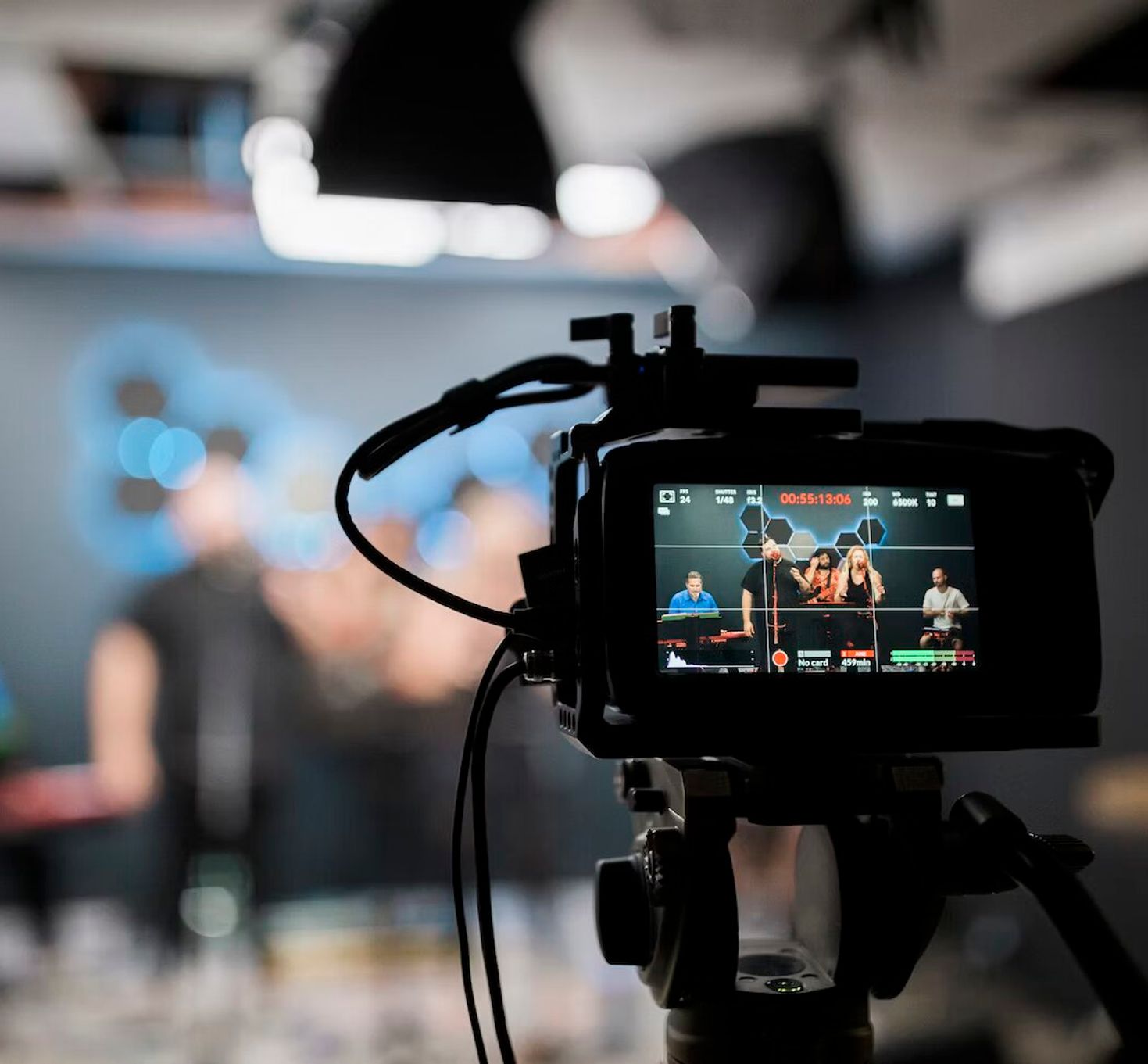
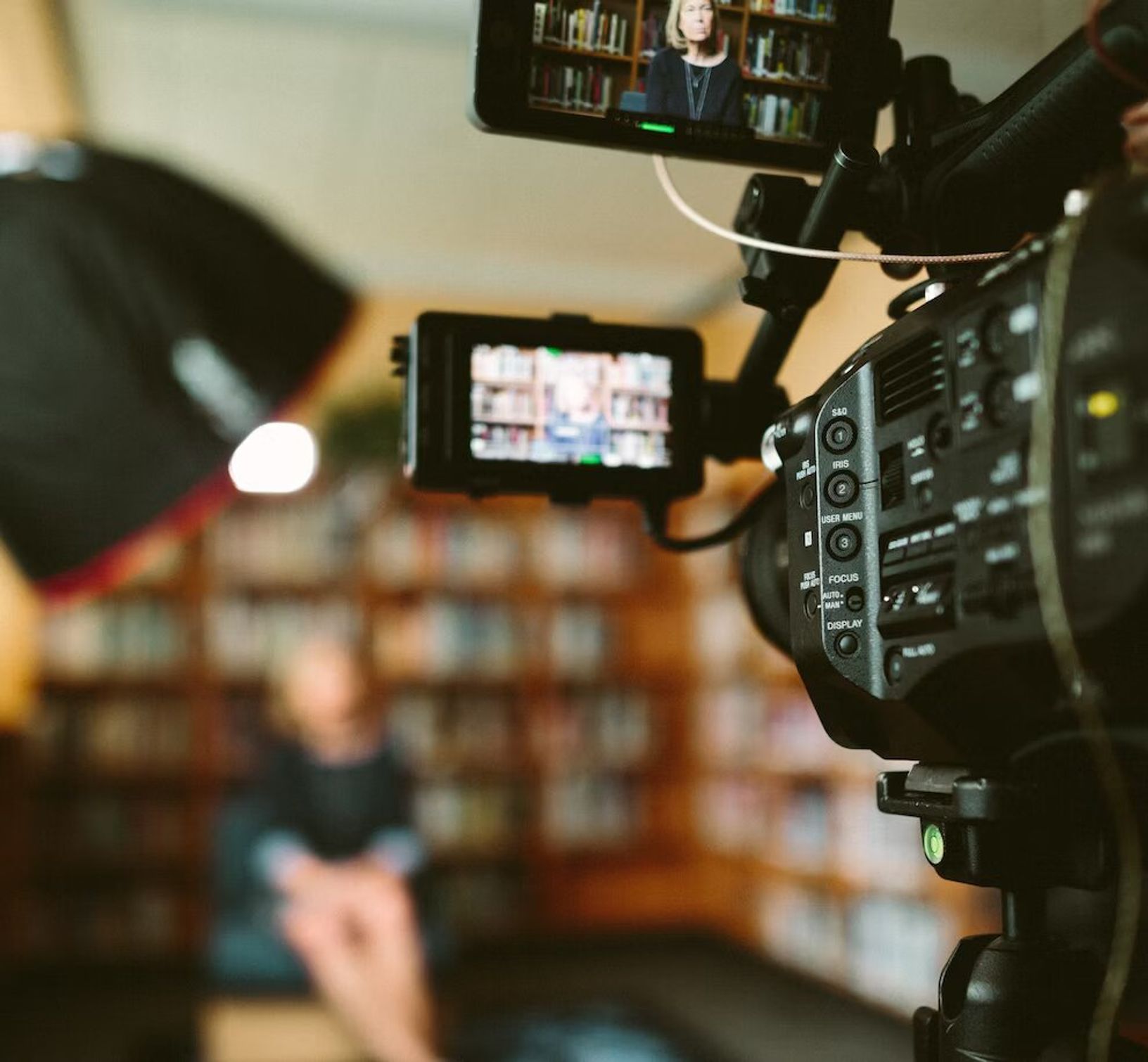
Understand how speaker labels and timestamps impact transcription and factors that slow down transcription.

Compare the best AI note takers for business leaders. See which tools handle accuracy, languages, privacy, and scale best in 2026.

A comparison of the best AI note takers for content managers. See which tools reduce editing, rewriting, and manual structuring across Teams, Zoom, and Meet.

Compare the best AI note takers for Microsoft Teams. See how they handle recording, summaries, security, and sharing and find the right one for you.

Learn how to create transcript from video quickly and accurately. Follow our simple steps to turn any video into searchable, editable text using HappyScribe.

Struggling with messy AI transcripts? Discover the 6 key factors that impact transcription accuracy and how to engineer better results today.



Looking for the best lecture recorder for students? I tested HappyScribe, Otter, OneNote, and others to see which app is accurate and creates the best study guides.

In depth review of Sonix, the transcription service: pros, cons, and features overview from actual users.

Find the best AI subtitle generator websites for YouTube and social media. HappyScribe reviews the best tools in the market to add subtitles and much more.
We reviewed the top transcription software for teams and agencies to help you work faster and stay organized. See the best tools for smooth collaboration.

Discover the top Any2Text alternatives for accurate transcription, subtitles, and workflows in 2026. Compare the best tools and pick the right upgrade.

Secondary market research saves time and money by using existing data to validate demand and uncover insights. Learn how to leverage it effectively.

Learn when recording without consent is legal, when it isn’t, and how privacy laws differ by state. Understand the rules before you hit record. Read now.

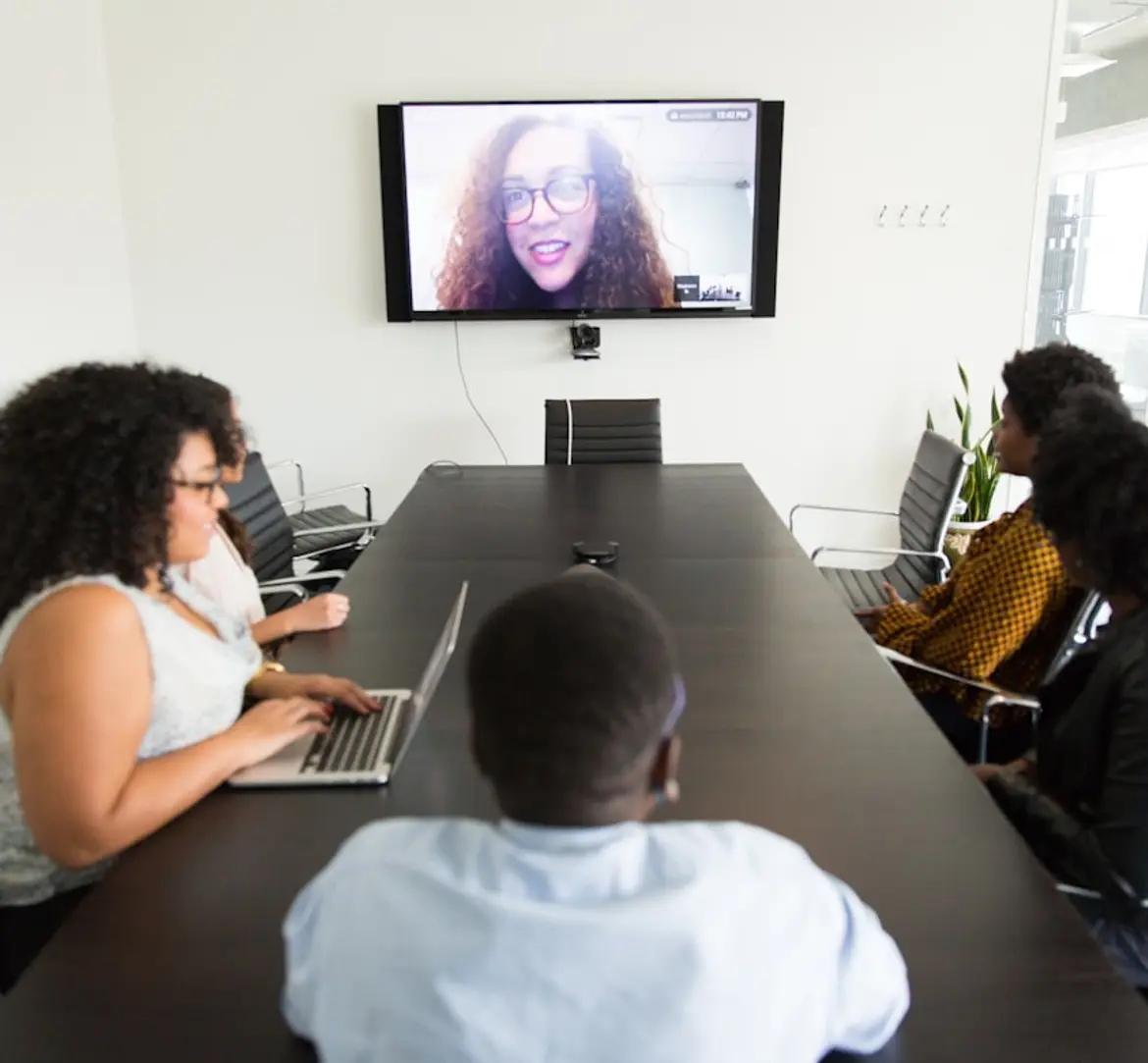
Learn how to record Microsoft Teams meetings in 2026 and discover an easier way to save, transcribe, and manage calls with HappyScribe’s AI meeting recorder.

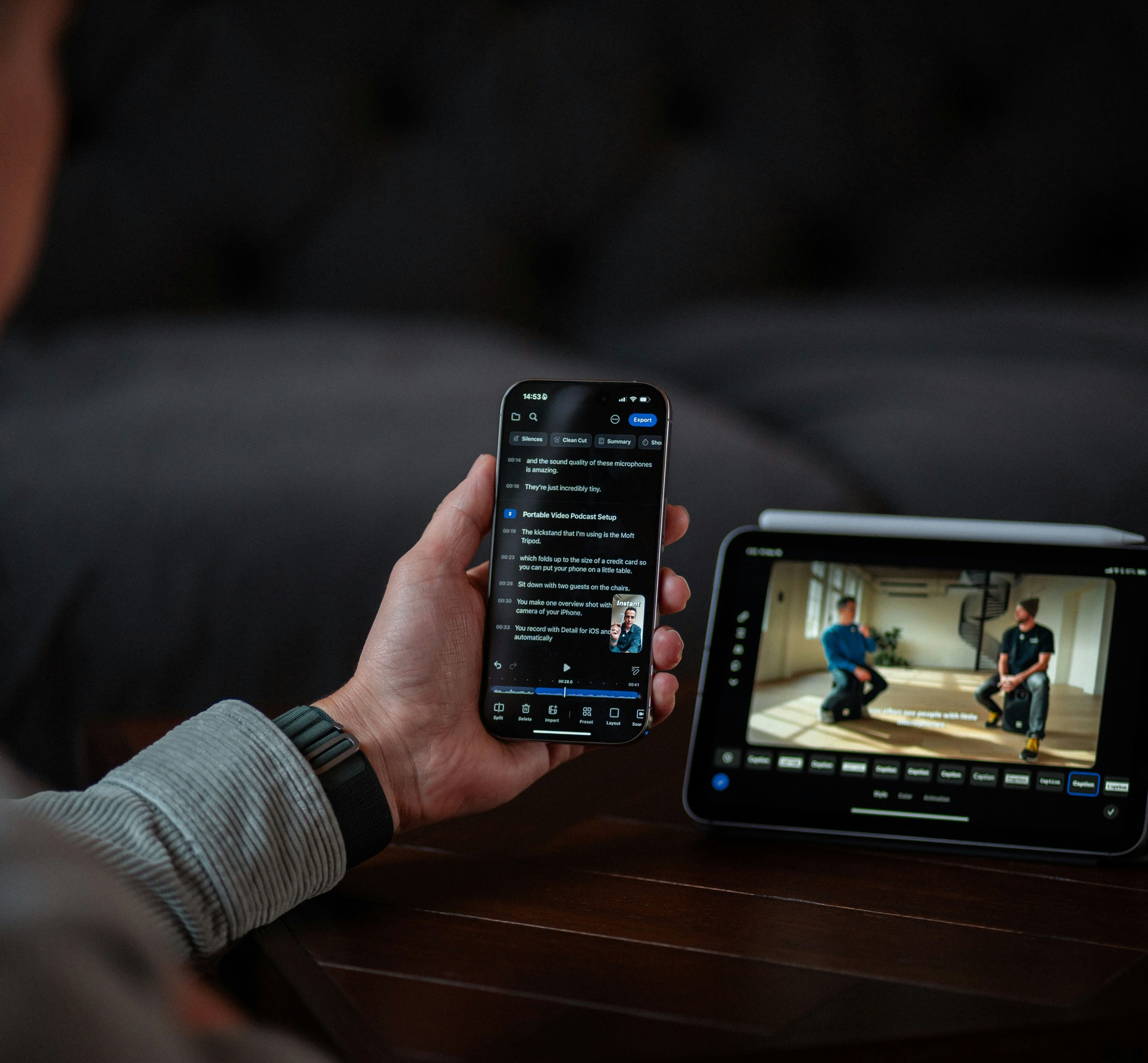
Compare the best podcast transcript generators for 2026 and see why HappyScribe is the top pick for accuracy, SEO, and repurposing.

Explore the top AI scribe tools and see how they improve clinical documentation, reduce charting time, capture meeting recordings, and ensure full security

Is HappyScribe worth it? Here’s an honest review of its features, pricing, real use cases, and limitations to help you decide if it’s right for you.

We tested the 5 best AI meeting note takers for teams and client calls, discover which tools deliver the most accurate summaries and boost productivity.

Discover the best podcast transcription software for 2026, including HappyScribe, Adobe Podcast, Descript, and more.

Check out 2026’s best speech-to-text tools. Full review of strengths, weaknesses, and who they suit best. Save time and choose wisely!

Looking for media transcription services that save time and stay accurate? Find top platforms with quick turnaround and reliable 2026 results.

Level up your 2026 creator workflow with 9 essential AI tools for transcription, editing, voiceovers, and distribution to publish more content in less time

Review top court transcription tools for legal professionals. See how HappyScribe and other tools handle accuracy, security, and speed.

Need a quick YouTube transcript? Compare the best methods and see how HappyScribe delivers the most accurate transcripts for creators and students.

Need a transcript maker that actually saves time? See which platforms deliver accuracy, speed, and clean editing workflows in 2026. Read the full guide.
Explore the top alternatives to Notta for accurate audio-to-text, smarter AI meeting notetakers, and more powerful workflows. Compare the best tools now.
Explore the best Veed alternatives for transcription, subtitles, and social-style editing. Find the right tool for your workflow today.

Stop wasting hours transcribing. We tested the 7 best AI transcription tools for accuracy, speaker ID, and language support. Find your fit here.
We compared Happy Scribe, Rev, Sonix, and Descript so you don’t have to. Here’s the ultimate AI transcription breakdown to help you choose the best fit.

HappyScribe offers highly accurate AI Subtitles and easy video translation in 120+ languages. Use the intuitive Subtitle Editor to polish timing and export to SRT or VTT files.

Explore the top AI meeting note takers for 2025, including HappyScribe, Jamie, Tactiq, Fireflies, and Otter. Discover their features, pros, and cons.
Discover the top Rev alternatives for 2026 - faster AI transcription, lower costs, multilingual support, subtitles, and better collaboration for modern teams.

Explore the best free audio transcription tools in 2026, from free plans to secure free trials. Compare HappyScribe, Gladia, MacWhisper, and more.

Looking for a quick way to summarize YouTube videos? Learn how to do it in seconds and compare the top AI tools for fast and reliable summaries.

AI tools for journalists must have a specific set of features to help you. HappyScribe reviews the best transcription tools for journalists available in the market.

Explore the best Descript alternatives in 2026. See how top platforms differ, where they fit, and which one aligns with the way you work. Read the guide.

Looking for a Clideo alternative? Compare top tools with better transcription accuracy, multilingual captions, and AI-powered workflows built for professionals.

Discover the 5 best business transcription services that turn meetings, client calls, and media recordings into accurate, secure, and ready-to-use transcripts.

Reach global audiences with the best AI video translator tools like HappyScribe, Rev, Smartcat, Maestra AI, and Wavel AI for accurate subtitles and voiceovers.

Explore the 5 best audio translator tools in 2026, including HappyScribe, VEED, DeepL Voice, and more, for accurate and secure multilingual audio translations

Compare TurboScribe alternatives like HappyScribe, Descript, Otter.ai, and Maestra AI to streamline transcription, translation, subtitling, and workflows.

What’s the ultimate best AI notetaker? I tested the two crowd favorites, Otter AI and HappyScribe, to see which one is the complete package.

Discover the top Trint alternatives for 2026. Compare HappyScribe, Otter.ai, Descript, Rev, and Sonix for accuracy, pricing, and professional workflows.

Looking for video to text software? Compare HappyScribe, Otter, VEED, Notta, and Tactiq, and see which one’s the best fit for your workflow.

I tested the top AI note taking tools so you don’t have to. Here are the top 5 AI note takers, what makes them the best, and the things you should consider when getting one.

Find the 5 best professional subtitling services in 2026. Compare HappyScribe, Rev, Amberscript, and more to find accurate, accessible, and compliant solutions.

Discover the top 6 human transcription services that offer high accuracy, data security, and expert-reviewed transcripts across industries.

Discover the best audio and video trimmers in 2026: free and paid. Compare speed, precision, formats, and features to cut, merge, and export clips fast.

Compare the top 5 AI transcription tools based on features, pricing, accuracy, languages, and exports so you can pick the best option fast.
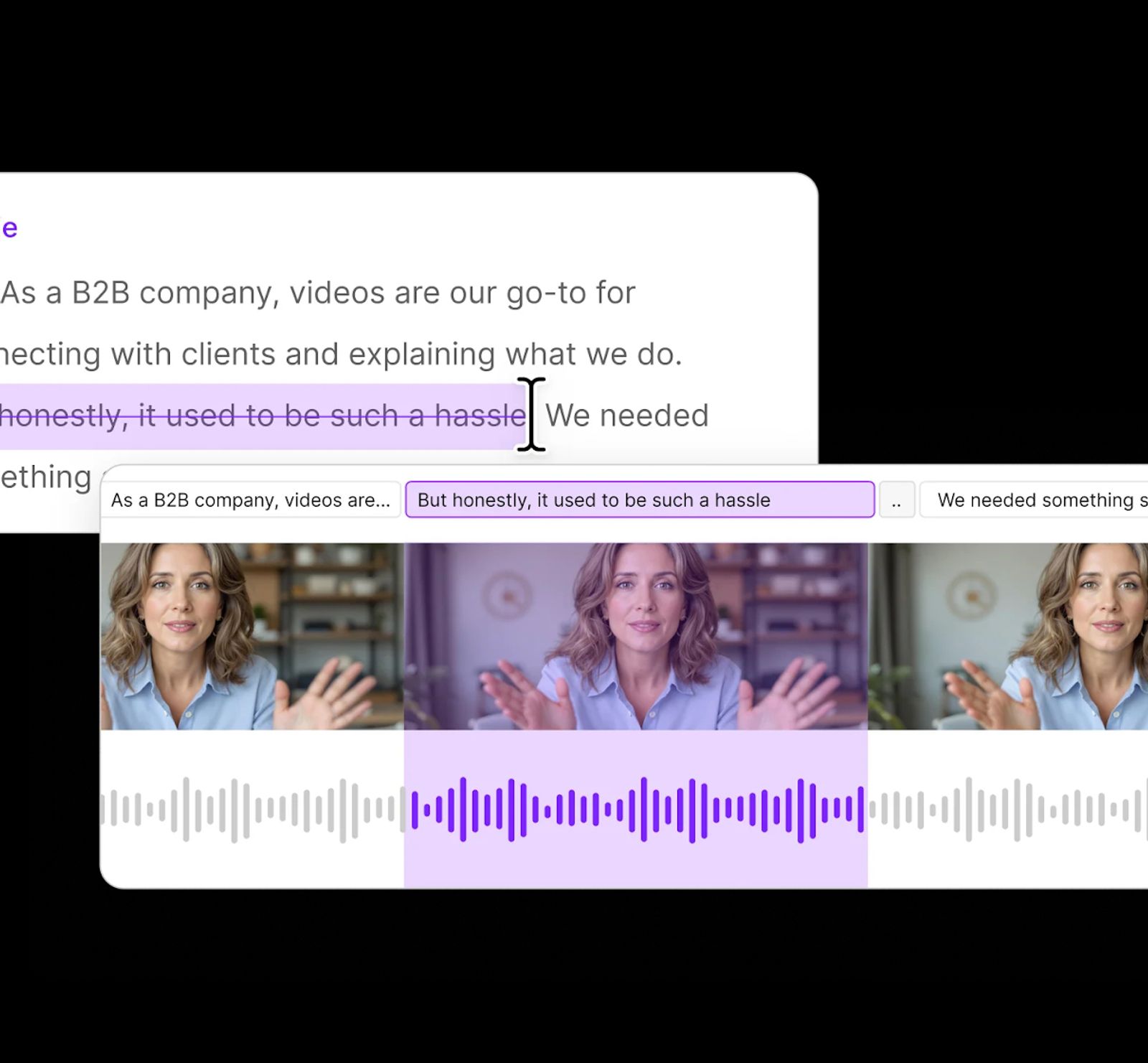
Discover the top 5 online voice recorders for 2026: free & paid. Compare audio quality, recording limits, formats, and collaboration to choose the best tool.

Discover the 5 best subtitle generators in 2026: HappyScribe, Veed, Canva, Sonix and Descript. Compare features, pricing, languages, accuracy to choose yours.

In this guide, we’ll explore the best free audio summarizer tools for 2026 (MP3 summarizers and AI-powered platforms built for meetings and podcasts. HappyScribe stands out as the best solution for professionals and students.

AI transcription software uses automatic speech recognition (ASR) to convert spoken words into accurate, editable text within minutes. In this article, you’ll discover the best AI transcription tools in 2026.

In this guide, we’ll break down what YouTube video summarizers do, compare the best video summarizer AI tools available in 2026.

This guide compares the top free (and freemium) options, outlines what features matter most, and shows why HappyScribe continues to be one of the most accurate and versatile AI-powered transcript generators available today.

In this guide, you’ll learn how these extensions work, what features matter, which add-ons are worth installing, and when it’s smarter to switch to a full transcript service like HappyScribe for better accuracy, formatting, and export options.

This guide will show you the easiest and most accurate ways to extract transcripts from YouTube videos for free, introduce the best tools available, and explain how HappyScribe stands out as a top solution for both free and professional transcription needs.

In this guide, we’ll compare the best free YouTube transcript tools, show you how to download YouTube transcripts, and explain why HappyScribe stands out as one of the most accurate and flexible options in 2026.

HappyScribe is a professional and efficient audio to text tool for businesses and content teams. Want to test it for yourself? Get started with a free trial.

Learn how to transcribe voice recordings to text quickly with AI tools. Convert lectures, interviews, and meetings into searchable documents. Step-by-step guide + tips for students, journalists, and professionals.

Google Meet Live Transcription improves accessibility with real-time captions. However, it struggles with accuracy, speaker attribution, and language limitations. Tools like Happy Scribe offer multilingual support and better transcription features for a smoother experience.

Google Meet has become a go-to tool for seamless online communication, whether you’re hosting a team meeting or a global webinar. But when it comes to documenting discussions and decisions, automation can save you time and effort while ensuring accuracy.

Transcription tools help Google Workspace users save time, boost accuracy, and streamline workflows by converting speech into text. Whether using built-in tools like Google Docs Voice Typing or AI-powered platforms like Happy Scribe, these solutions make meetings, interviews, and content creation more efficient, accessible, and collaborative.

Google Meet makes it easy to connect, but what if language gets in the way? Its built-in transcription feature converts speech into text in multiple languages, making meetings more inclusive, searchable, and accessible for global teams, educators, and businesses.

Google Meet’s recording feature makes it easy to capture important meetings, online lectures, and virtual discussions for future reference. But to get the most value from these recordings, converting them into text can boost accessibility, improve productivity, and make information easier to search and share.

AI transcription has revolutionized the way we document Google Meet conversations, providing speed and accuracy that far outpace traditional methods. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to set up and leverage AI-powered tools like Happy Scribe to transcribe your meetings effortlessly and efficiently.

Google Meet automated note-taking saves time and ensures you never miss important meeting details. With tools like Happy Scribe’s AI notetaker, you can effortlessly capture, organize, and review discussions, boosting productivity and collaboration.

Google Meet has become a go-to video conferencing tool, making communication and collaboration effortless. But if you need transcriptions to capture meeting discussions, understanding Google Meet’s transcription pricing is key to staying on budget and optimizing your workflow.

Research suggests that millennials and Gen Z viewers have made captions and subtitles a regular part of their viewing experience, both by choice and sometimes out of necessity. This article discusses the trends and benefits of captions and subtitling for younger audiences.

In this article, you’ll learn how meeting transcription services can streamline your production workflow, ensure nothing gets lost in translation. We’ll explore the advantages, limitations, and key factors to consider, helping you decide if transcription tools are the right choice for your media projects.

In this article, you’ll learn the key differences between verbatim and edited transcription and how to decide which one best suits your needs.

In this article, you’ll learn how to efficiently convert video content into text, whether for accessibility, SEO, or broader audience engagement. We’ll explore top tools like Happy Scribe, and offer practical tips for ensuring accurate and high-quality transcriptions to make your content conversion process smooth and effective.

In this article, we’ll walk you through the differences between VTT and SRT subtitle formats, so you can pick the one that works best for your video. Whether you’re after sleek, styled captions or just need something simple and widely compatible, we’ve got you covered!

A comprehensive guide on understanding Spotify for podcasters, from submission to promotion.

In this article, we’ll dive into the importance of high-quality audio in recordings. Whether you're creating a podcast, video, or music, we’ll walk you through essential steps to make sure that your audio is clear, professional, and keeps your audience engaged, with a few handy tips from HappyScribe along the way.

This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to convert video content into text. It discusses the basics of video content conversion, the benefits, the top tools for transcription like HappyScribe, and offers tips and tricks.

In this article, we’ll dive into why subtitles are important for your Instagram Reels and how they can improve your content. You’ll learn how tools like Happy Scribe can help you easily add captions to your videos, making them more accessible and engaging for a bigger audience.

How can someone tell whether MT is accurate or not? This article explores the different ways in which MT accuracy is evaluated, listing a range of metrics and approaches that are used to gauge quality, both based on human expertise and automated metrics.
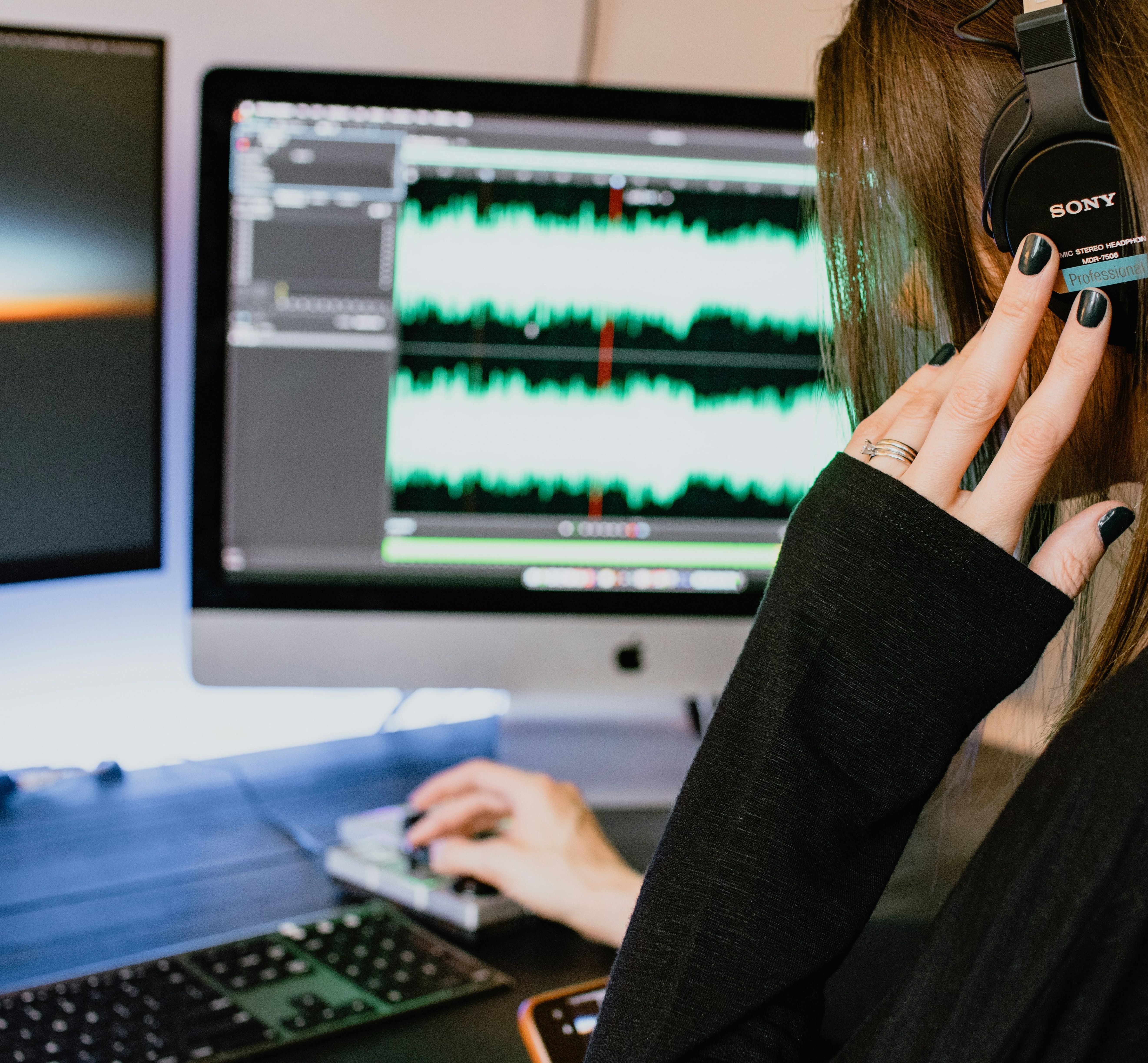

In this article, you’ll discover how using a solution like Happy Scribe’s AI- and human-assisted transcription can drastically cut down production time while boosting the quality of your transcriptions. Learn how accuracy in ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) is measured, what factors influence it, and how every improvement translates to time savings and better content workflows.

An analysis of eye movements as people read subtitles? That sounds like scientific experimentation, but in fact, researchers are using viewing patterns, or “eye tracking technology,” as a tool to make subtitling more effective. This article provides an overview of how researchers are using this information to better understand what viewers focus on while watching a screen, including text, images, and other visual cues. Researchers then apply this knowledge to improve subtitle placement, formatting, timing and more!

Shot changes - transitions between different camera angles, scenes, or locations - are fundamental to storytelling in video, but also pose unique challenges for subtitling. We’ll dive deep into what shot changes are exactly and why they’re super important for providing top-quality subtitles.
Happy Scribe's Quality Centre ensures high-quality, distribution-ready subtitles and transcripts with minimal revisions. Our Quality Centre, featuring subtitling Style Guides and Glossaries, also includes advanced settings like subtitle timing presets, transcription customizations, and more.

With the Gen 2 Model from the voice-to-text technology startup, the time to refine subtitles is reduced by 13%, and the error rate drops by 8%. "This will be a game-changer for content creators worldwide."

Discover why the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are crucial for subtitling and transcription, helping media companies ensure inclusivity and reach a wider audience. This article explains how WCAG standards support the deaf and hard-of-hearing community with high-quality, accurate subtitles. Learn how following these guidelines can improve your content’s accessibility and create a more inclusive digital experience. Written by Henni Paulsen, June 2024.
In this article, you'll learn all about the European Accessibility Act (EAA) and its requirements for making audiovisual content accessible through subtitles and captions. It also explains how automating the subtitling process can save you time and money, improve accessibility, and engage a broader audience. Article written by Henni Paulsen, June 2024.

Meet Happy Scribe at GALA's signature event for the globalization and localization industry, on 21-23 April 2024 in Valencia, Spain.

In this article we explain the differences between adapting and translating your subtitles. Find out what works best for your audiovisual content!

This article examines the complexities of creating effective and accurate SDH subtitles, highlighting the technical, linguistic, and cultural challenges involved in making media content accessible and inclusive for all viewers.

This article explores SDH subtitling as a complex art that enriches the viewing experience for the deaf and hard of hearing by blending dialogue, sound effects, and emotional depth. It discusses foundational aspects, methods, obstacles, and technological advancements in SDH subtitling, emphasizing the critical roles of precision, timing, and comprehensive audio cues, and anticipates the use of AI and cloud technology to improve subtitling accessibility and efficiency.

This article provides a step-by-step guide on creating SDH subtitles for movies, offering tips and techniques on how to make them accessible and visually appealing to viewers.

Happy Scribe is thrilled to announce a new partnership with GALA, The Globalization and Localization Association, where Happy Scribe provides English subtitling services for GALA’s videos in 2024.

This blogpost discusses three simple methods for SaaS companies to convert audio to text. It highlights the benefits of using transcription services, automated speech recognition software, and manual transcription. The post aims to help SaaS companies save time and improve their productivity.

This article compares the effectiveness of AI and human subtitling for educational and academic content. It explores the pros and cons of each approach, highlighting the accuracy, efficiency, and cost factors. Ultimately, it poses the question of which method is more efficient for accurate subtitling in educational contexts.

Video content plays a crucial role in acquiring customers. It helps businesses engage with their target audience effectively and showcase their products or services. Videos are more engaging and informative, making them a powerful tool for customer acquisition. Marketers should prioritize creating high-quality video content to drive growth and conversions.

Subtitles in virtual classes can enhance accessibility and learning experiences. Use clear fonts and colors, place them at the bottom of the screen, and ensure accurate captions. Encourage students to provide feedback on subtitle preferences and make adjustments accordingly.

This blog post explores the challenges and opportunities in using AI for subtitling in language services. It discusses how human expertise and AI can be combined to improve efficiency and accuracy in subtitling, highlighting the importance of finding the right balance between human and machine capabilities.

Subtitling educational videos in universities can benefit multilingual audiences in various ways. It improves comprehension, allows non-native speakers to follow along, supports accessibility for the deaf and hard of hearing, and aids in language learning. Subtitles also enable better retention of information and create a more inclusive learning environment.

This blog post discusses the evolution of subtitling technology and its implications for higher education. It explores how advancements in technology have made subtitling more accessible and accurate, benefiting both students and educators. The post also highlights the potential impact of these advancements on language learning and accessibility in education.

This blogpost discusses the potential benefits of real-time subtitling for academic events and seminars. It highlights the accessibility and inclusivity advantages, as well as the potential for enhancing understanding and engagement among attendees. The post also considers the challenges and solutions for implementing real-time subtitling technologies.

This blogpost emphasizes the significance of cultural sensitivity in subtitling for international students in universities. It highlights the need to consider cultural nuances and adapt subtitles accordingly to ensure effective communication and understanding.

This blogpost discusses the importance of providing subtitles in education to make it fair for students in international schools and universities. It highlights the benefits of subtitles for students with hearing impairments and those who speak English as a second language.

This blog post discusses the benefits of using subtitles in research and conference videos to make them accessible and shareable worldwide. Subtitles can help overcome language barriers and improve accessibility for individuals with hearing impairments, making the content more inclusive and reaching a broader audience.

This blogpost discusses the importance of subtitles in making academic and educational videos accessible to a wider audience. It explores the benefits of subtitles and provides tips on how to effectively add subtitles to videos.

Automated subtitles offer a cost-effective and time-saving solution in education. They enhance accessibility for students with hearing impairments and second language learners.

This blog post highlights the importance of using captions for companies in various contexts. It emphasizes how captions can enhance accessibility, engagement, and search engine optimization. Additionally, it discusses the features and benefits of using Happy Scribe, a captioning and transcription tool.

This blogpost discusses the potential of AI subtitling in global media to enhance multilingual accessibility. It explores the benefits of AI technology for improving accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness in creating subtitles. The future looks promising for leveraging AI in making content more accessible across languages.

Controlling language quality in AI-powered subtitling is important for accurate and effective communication. This blog post provides tips on how to maintain high language standards, including training the AI model with quality data, using proper punctuation and grammar, and regularly reviewing and refining the subtitles.

This blogpost discusses how artificial intelligence (AI) is being utilized to expedite subtitling in language services. It explores various AI techniques and tools that are employed to automate and improve the subtitling process, resulting in faster and more efficient translation and localization services.

This blog post explores the various aspects of professional captioning workflows. It covers topics such as best practices, tools, and technologies involved in captioning, making it a valuable resource for professionals in the captioning industry.

This blog post discusses the impact of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Machine Translation (MT) on subtitling. ASR and MT technologies have made subtitling more efficient and accurate, but there are still challenges such as accuracy, style, and cultural context that need to be addressed.

This blogpost provides insights into the media localization sector, with a focus on subtitling and captioning. It discusses the industry's growth and the importance of these services in reaching global audiences. The post also covers trends, challenges, and best practices for content localization in the fast-evolving media landscape.

Business transcription involves converting audio or video recordings of meetings, interviews, or market research into written text. This service provides accurate records that can be easily referenced, shared, or analyzed, saving time and improving productivity for businesses.
This blogpost explains how AI-driven subtitling can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of language service providers. By automating the subtitling process, AI technology can save time and reduce errors, leading to improved productivity and customer satisfaction.

Advanced captioning is revolutionizing the language industry by providing accurate and real-time translations of spoken content into text form. This technology is benefiting various sectors, including media, education, and accessibility services, by making audio and video content more inclusive and accessible to a wider audience.

This blog post offers tips and tricks for language professionals on how to create perfect captions. It provides helpful insights on crafting engaging and effective captions that enhance the communication and impact of their work.

This blogpost discusses the impact of machine learning and AI on subtitling services, highlighting the benefits of these technologies in improving accuracy and efficiency. The use of advanced algorithms and automated processes is revolutionizing the language services industry.

This blog post discusses the increasing importance of subtitling and captioning in multilingual media. It highlights their role in ensuring accessibility, reaching broader audiences, and improving understanding. Subtitles and captions have become essential tools for media creators to engage viewers from different languages and cultures.

This blogpost offers helpful tips for language service providers to improve subtitling services. Topics include timing, length, readability, accurate translations, and software tools. Following these tips can enhance the overall quality and experience of subtitles for viewers.

Finding the best transcription services for research projects can be a daunting task. However, three top choices include Rev, TranscribeMe, and GoTranscript. Rev offers accurate transcriptions with quick turnaround times, while TranscribeMe specializes in high-quality voice-to-text services. GoTranscript provides affordable options with multiple file formats supported.

AI technology is revolutionizing the field of subtitling, allowing for personalized and customized solutions in language services. By utilizing AI, companies can provide accurate and tailored subtitles that meet individual needs and preferences, enhancing the overall viewer experience.

At Happy Scribe we have a team of 6 Product Engineers building and maintaining a web application that serves 500k users per month. One of our secret tools: Ruby on Rails.

This blog post discusses the benefits of using cloud-based and software platforms for subtitling, such as increased efficiency, accessibility, and collaboration capabilities. These platforms can streamline the subtitling process and improve overall productivity for content creators.

This blogpost explains Vimeo's fee structure for creators, highlighting the different membership options and the costs associated with each. It provides a clear breakdown of pricing and features, helping aspiring creators make informed decisions about their video hosting platform.
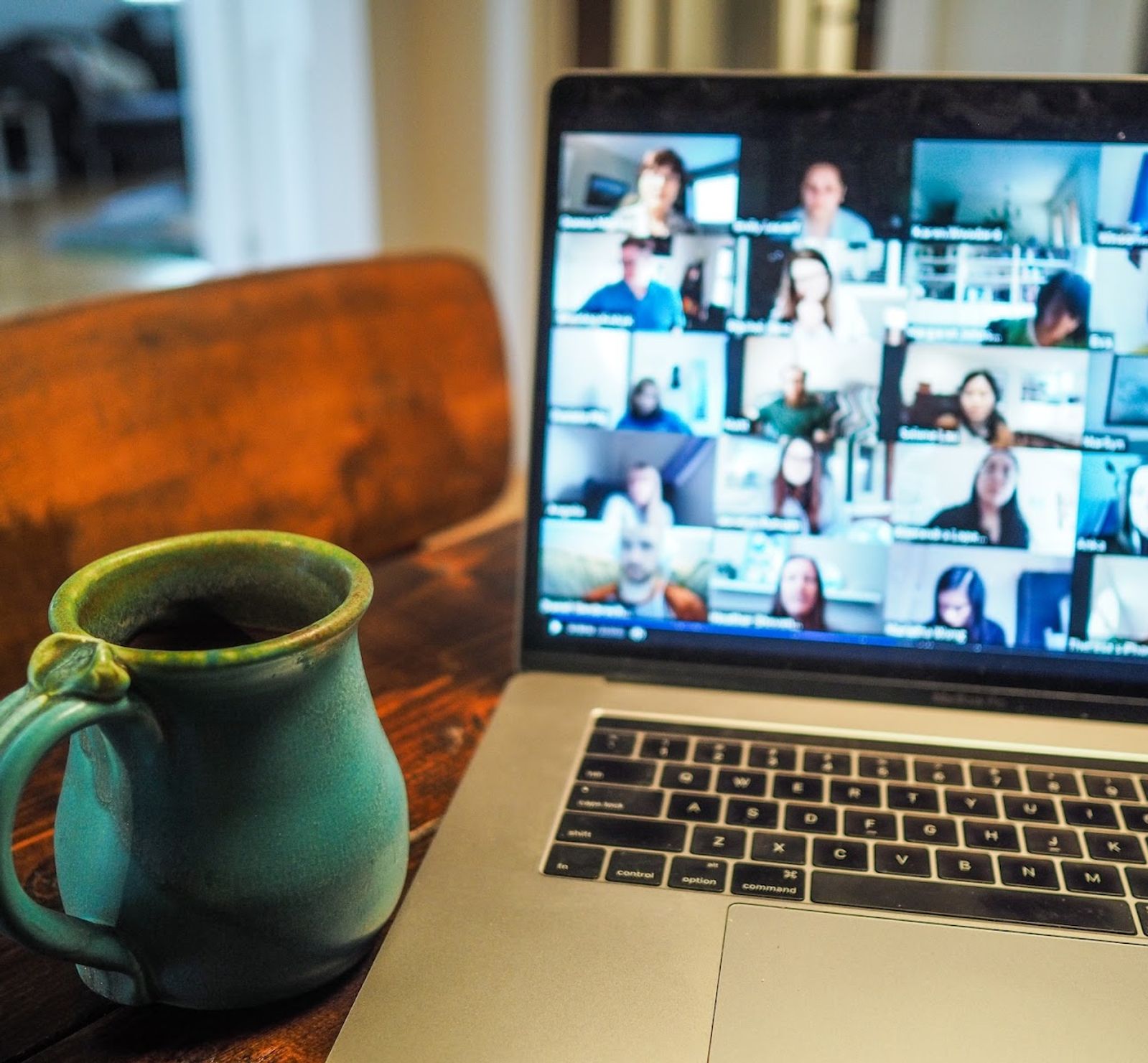
Zoom meetings are now essential; transcripts enhance efficiency and accessibility.

If you want to download videos from Vimeo, you can use various online tools such as SaveFrom.net, Video DownloadHelper browser extension, or the 4K Video Downloader software. These tools will allow you to easily save Vimeo videos for offline viewing.

In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about Zoom Cloud—how it works, its features, and a few common issues you might run into, along with tips to solve them. Let’s dive in!

Yes, Zoom has a feature called Closed Captioning that can display translated subtitles. Hosts or participants can enable this feature and select the language for the subtitles. It's a useful tool for multilingual meetings or webinars.

This blog post provides a step-by-step guide on how to translate subtitles on Zoom. It covers the process of enabling the real-time transcription feature, selecting the language for translation, and adjusting subtitle settings for optimal viewing. Helpful tips and troubleshooting suggestions are also included.

Transcribing interviews can be time-consuming, but there are ways to do it faster. Learn how to transcribe interviews and use transcription tools like HappyScribe.

Timing is crucial in professional subtitling. Proper synchronization between the audio and subtitles enhances viewer experience. Subtitles should appear and disappear at the right moment to ensure clarity and readability. Timing also affects the overall flow and comprehension of the content being subtitled.

Crafting an effective video script involves determining the objective, identifying the target audience, creating a compelling storyline, using clear and concise language, and incorporating visuals and sound to enhance the message. A well-crafted script can engage viewers and effectively convey your message in a video.
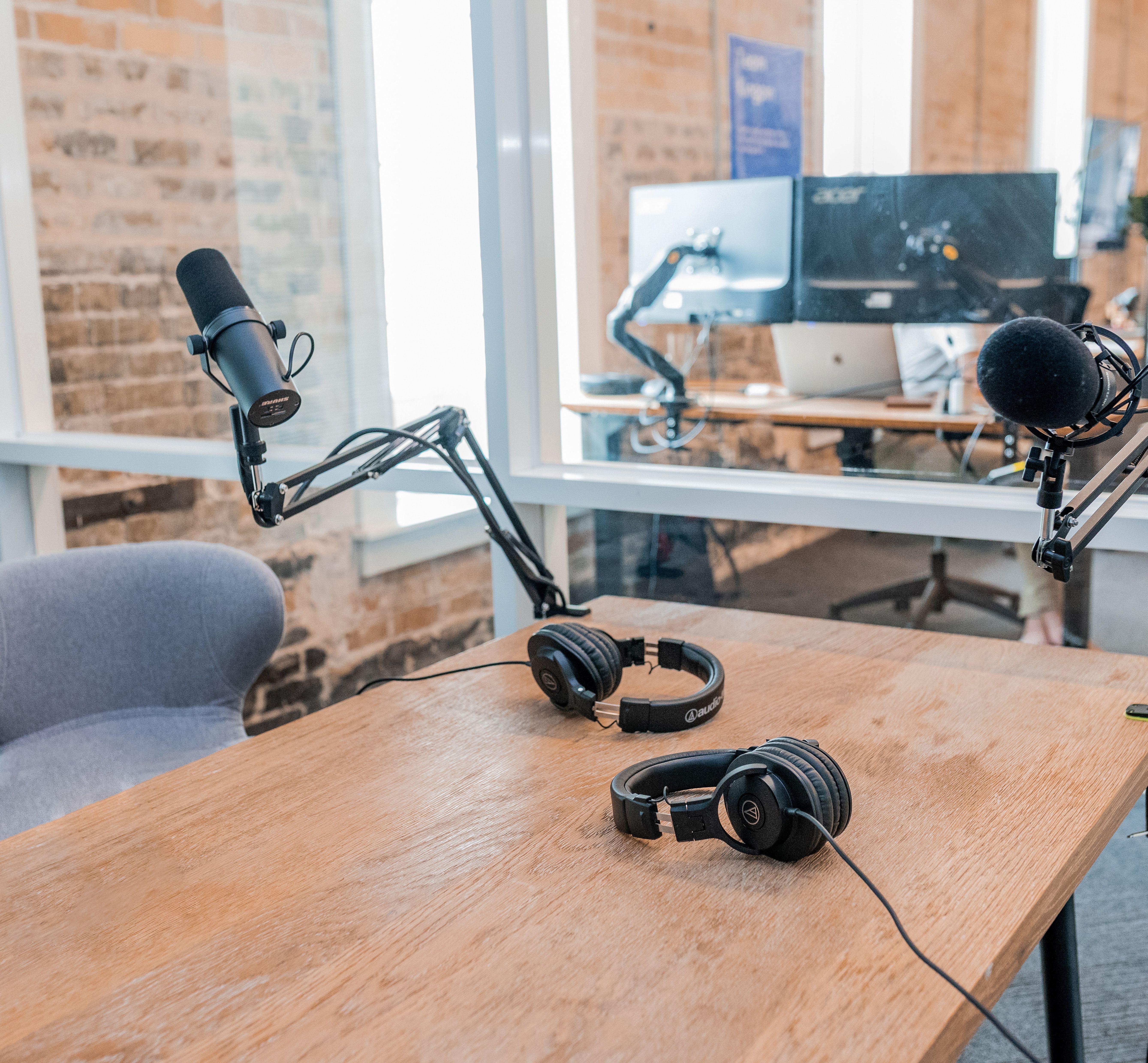

This guide outlines the key steps to launch a successful podcast. It covers topics such as choosing a niche, purchasing equipment, recording and editing, creating engaging content, promoting your podcast, and monetizing it. Whether you're a beginner or have some experience, this guide has you covered. Happy podcasting!

Thinking about exiting the cloud for cost savings yet reluctant to staff up an ops team? We've gone for an intermediate step that has saved the majority of our costs without adding much operational overhead.

This blogpost discusses the latest innovations in corporate subtitling and transcription services. It covers advancements such as AI-powered transcription tools, automated subtitling software, real-time captioning solutions, and improved accuracy and efficiency in transcribing and subtitling content.

Wondering how to tackle the obstacles of remote work? Audio transcription software has a load of benefits. Read about them here and try the HappyScribe AI Notetaker for meetings.

Streamlining Subtitle Editing: A Team Approach

Captions in Tech: Enhancing Communication and Engagement

Maximizing Sales Strategy and Growth Through Effective Transcription

Interpretations in International Market Research: Bridging Language Barriers for Business Expansion.

Unraveling the Top Benefits of Subtitles for Your Business

Captions help improve the engagement and training value of videos. Here, we break down how to create and use subtitles for employee training materials.

Subtitles in Business: A Key to Enhanced Communication and Engagement.

Transcriptions: Transforming User Experience Research into Actionable Insights.

Discover how subtitles revolutionize global business communication, fostering clarity and inclusivity in an interconnected world.
Explore how enterprise subtitle generators enhance video content accessibility and reach in a globalized business world.

Do you need Spanish subtitles for your videos? Learn how to translate and transcribe English audio quickly while maintaining contextual accuracy.

Automatic transcription refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technology to convert spoken language into written text. Learn how to use AI for qualitative research transcription with HappyScribe.

Exploring Qualitative Research Interviews: From In-Depth Analysis to Practical Transcription Techniques

Video transcription revolutionizes educational research by enhancing data precision, accessibility, and analytical depth. Tools and software for converting video to text are used in academic resarch.

Transcription in qualitative research transforms spoken dialogues into script, enhancing analysis and accessibility.

Understanding Transcription's Impact on Qualitative Research Accuracy

The three main types of transcription in qualitative research include verbatim transcription, intelligent transcription, and edited transcription. Make transcription easy with tools like HappyScribe.

Guide to explore the role of transcription in qualitative research, highlighting its methods, challenges, and impact on outcomes.

Happy Scribe debuted at LocWorld50, San Jose, highlighting AI's role in reshaping localization and emphasizing the balance between technology and human touch in localization.

Understanding the concept: what is collaborative captioning and subtitling?

Delve into the intricacies of interview transcription, from capturing speech details to employing the best editing tools and techniques for polished results.

Step-by-step guide to transcribing an interview, editing it and using the best software to reach your audience. Get the best interview transcription for journalist, researchers and more.

Themes and tags are pivotal tools in qualitative research, helping organize and extract vital insights from interview data.

Interview transcription converts spoken content into written form, with factors like audio quality and length influencing cost; various methods exist, including automated transcription services like HappyScribe.

Explore the essentials of selecting equipment, recording high-quality interviews, and optimizing the interview transcription process for clarity and accuracy using AI and online software.
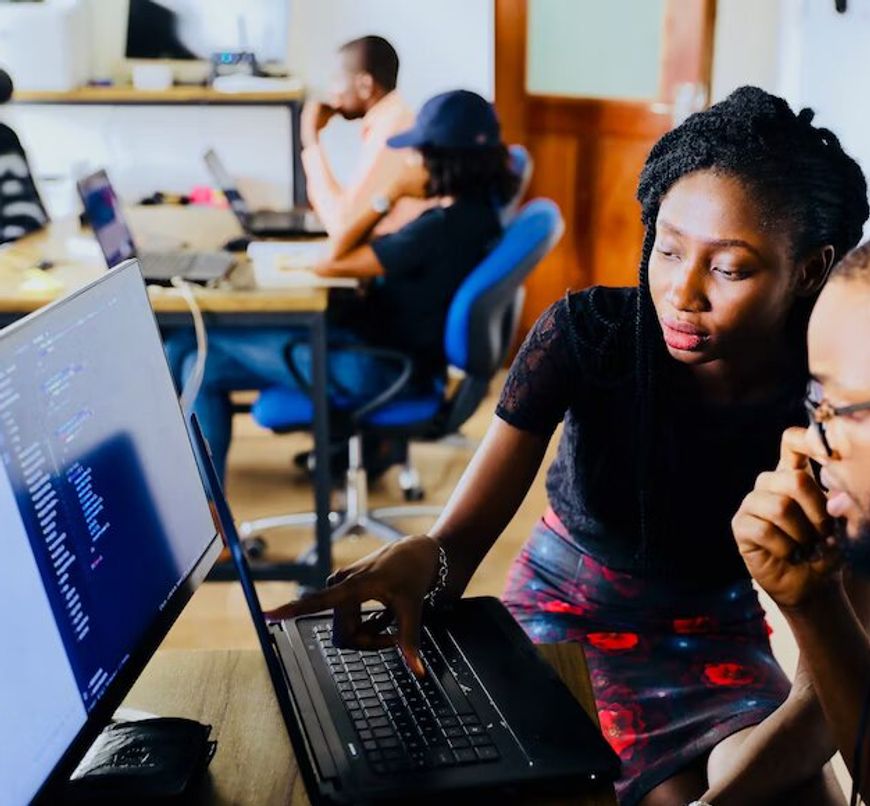

Delving into transcription: From influencing factors to the role of technology and tips for faster processes.
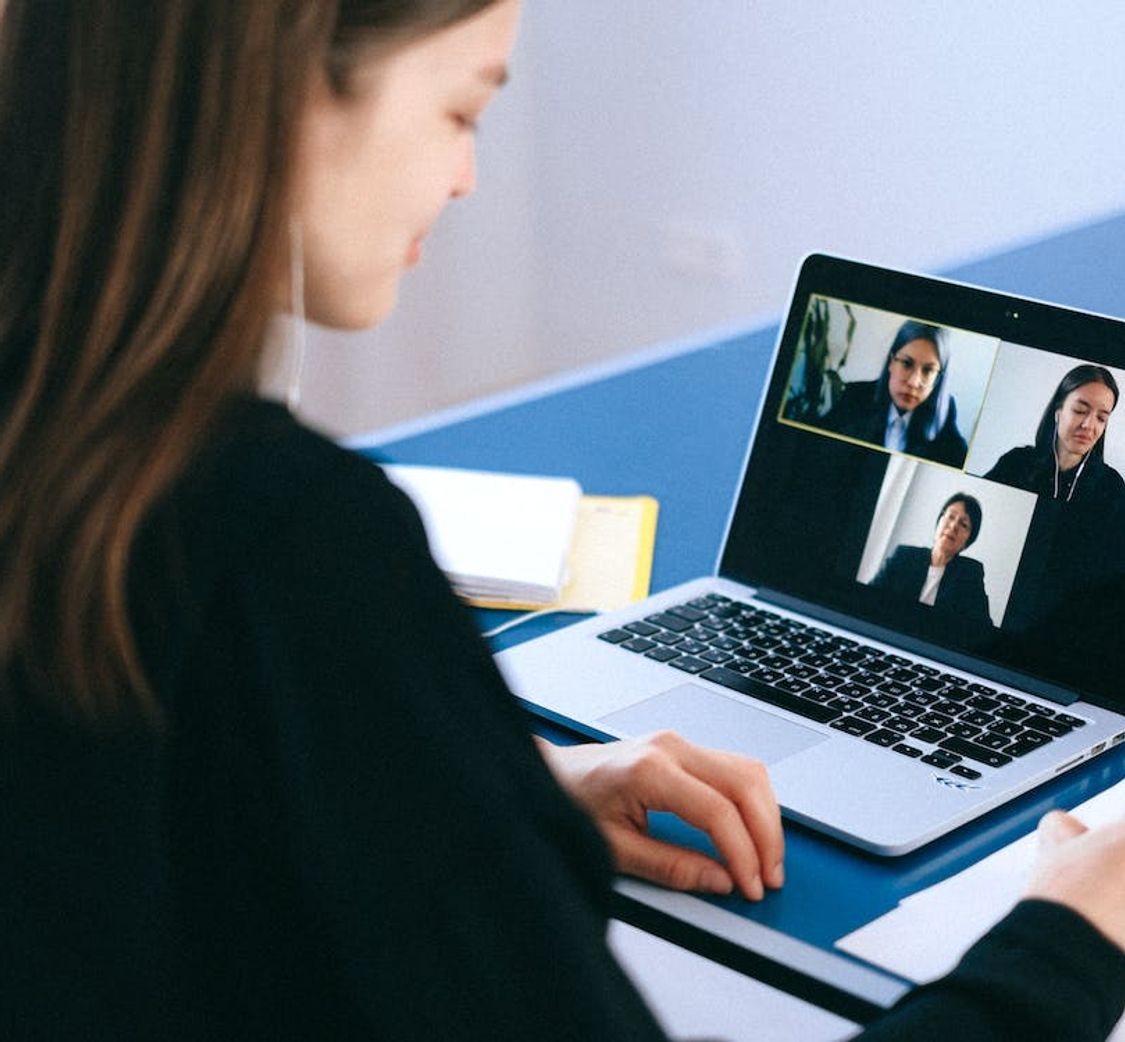

Maximize your Zoom meetings' potential by converting recordings for accessibility and seamless collaboration.

Discover the power of Zoom's transcription feature and elevate your virtual meeting experience.

Navigating the digital age, this article delves into retrieving Zoom recordings and enhancing the experience with transcription and captioning services.

Navigating the virtual realm? This guide simplifies joining Zoom sessions, ensuring seamless connection across devices and platforms. Dive in!

The shift from in-person to virtual meetings has revolutionized business communication. Dive into the Zoom era and its benefits.

Discover the critical role of language interpretation in Zoom webinars for inclusive, effective, and global communication.

Delve into the game-changing world of YouTube subtitles and discover how tools like Happy Scribe can skyrocket your content's impact and reach.

In our rapidly globalizing world, content producers must bridge linguistic gaps while ensuring accessibility. Subtitles aren't just a tool; they're a necessity. Dive into the significance of subtitling, its potential to captivate global audiences, and discover how tools like Happy Scribe can make it all seamless.

Harness the power of Happy Scribe for precise transcription, subtitling, and translation, bridging language barriers in global media.

Harness the power of automation and organization in media libraries, ensuring efficient subtitling and transcription with Happy Scribe's tools.

Webinar replays have revolutionized how we access, engage, and benefit from online presentations, making Zoom meetings more flexible and inclusive.

In today's remote-focused world, effective Zoom note-taking is crucial to capture every vital insight during virtual meetings.

Leverage Zoom's capabilities beyond meetings by mastering its transcription and note-taking potential, enhancing your productivity.

In today's digital era, translating Zoom recordings is vital for global reach. Using tools like Happy-Scribe, this process is now seamless, ensuring effective communication across diverse audiences.

Navigating the global landscape, free Zoom recording translations unlock limitless collaboration. Discover how to bridge language barriers efficiently.

Explore voice translation from Zoom recordings using tools like Happy Scribe.

With the rise of Zoom, many are seeking efficient ways to auto-capture meeting insights. Dive into the world of automatic note-taking on Zoom.

In the Zoom era, efficient note-taking ensures better decision-making, continuity, and accessibility for meeting attendees. Learn how to optimize this essential task.

In today's digital era, translating subtitles in Zoom recordings promotes inclusivity. Discover how to achieve this step-by-step with Happy Scribe and other tools.

AI-powered note-taking tools for Zoom, focusing on the benefits, best practices, and the powerful capabilities of Happy Scribe, a premier Zoom transcription service.

In 2026, video meetings are paramount; mastering the art of accurate minutes is your ticket to seamless business operations.

Discover the subtle signs of clandestine recordings and the significance of safeguarding privacy in our digitally entwined world.

Delve into the pressing privacy concerns of Zoom meetings and the measures to ensure secure digital communication.

Discover how to seamlessly integrate third-party subtitling services into your Zoom meetings for enhanced communication.

Harness the power of Zoom's subtitle capabilities to enhance communication, inclusivity, and engagement during virtual meetings and webinars.

In the evolving digital landscape, Zoom recordings have revolutionized the way we relive and revisit virtual interactions, offering convenience and accessibility across devices.

Whether for professional collaborations or personal gatherings, knowing how to effectively record Zoom sessions is crucial. With the options of free and paid plans, Zoom caters to a variety of needs, ensuring that no moment is lost.

With video conferencing booming, understanding Zoom's pricing for webinars is crucial. Dive in to discern free versus premium options.
Deciphering Zoom's Pricing: Navigating Between Free and Paid Options for Optimal Virtual Collaboration.

Unlocking the Power of Zoom Rooms: A Deep Dive into Features, Accessibility, and Seamless Integration of Subtitles.

Enhance Zoom accessibility with subtitles and captions: a step-by-step guide for seamless communication.

Discover the essentials for ethically recording Zoom meetings, prioritizing privacy and optimizing team collaboration.

Unlock the power of Zoom subtitles for enhanced communication, inclusivity, and a seamless virtual meeting experience.

Enhance your Zoom recordings with accurate subtitles using third-party tools for better accessibility and comprehension.

Discover efficient techniques to trim and enhance your Zoom recordings for a more engaging audience experience.

Discover how to plan, execute, and enhance Zoom webinars for impactful engagement and global reach. Dive into our comprehensive guide now!

Explore the features and benefits of Zoom Meetings, and learn how Happy-Scribe enhances accessibility through accurate transcriptions and captions.

As Zoom's global prominence rises, the need for comprehensive translation tools in diverse virtual gatherings becomes increasingly paramount.

Zoom's versatility extends beyond conferencing, with tools like Happy Scribe enhancing its capabilities, especially in transcription services.

As Zoom transforms global communication, overcoming linguistic barriers becomes paramount, highlighting the need for webinar translations.

Amidst the digital age, Zoom's rise and its integrated interpretation feature have revolutionized global communication, but third-party translation remains crucial.

Embrace Zoom, the preferred virtual communication tool, and discover its seamless integration with live translation for globalized meetings.

Explore the realm of live translation apps for seamless multilingual meetings and events in our digital age.

In today's digital era, understanding Zoom's diverse offerings—meetings and webinars—is essential for optimized online interactions. This guide elucidates their distinct features and applications.

Dive into the transformative world of Zoom Webinars with this guide, unlocking the platform's potential for global outreach and engagement in our virtual era.

Navigate the world of Zoom Webinars with this comprehensive guide, ensuring an enriching experience for attendees in our evolving virtual landscape.

Explore the comprehensive guide to efficiently sharing Zoom recordings via email, optimizing virtual collaboration in our increasingly digitalized world.

Discover how to seamlessly integrate Google Translate with your Zoom calls, enhancing communication across various languages for a more inclusive experience.

Amidst Zoom's surge in popularity, non-host attendees often wonder how they can record sessions. This guide delves into ethical, legal, and technical considerations for non-host Zoom recording.

Enhance your Zoom experiences by seamlessly recording sessions and transcribing them effortlessly with Happy Scribe. Dive into our detailed guide below.

Discover how to effortlessly record Zoom sessions on your mobile devices with this comprehensive guide.

Zoom's rise in remote work is revolutionized by real-time translation, ensuring global inclusivity.

Zoom: Revolutionizing communication with real-time translation and transcription.

Vimeo provides unique video-sharing capabilities, prioritizing privacy and quality, making it the choice for professionals and creators.

In the digital age, privacy reigns supreme; Vimeo steps up, ensuring users have unparalleled control over their video content.
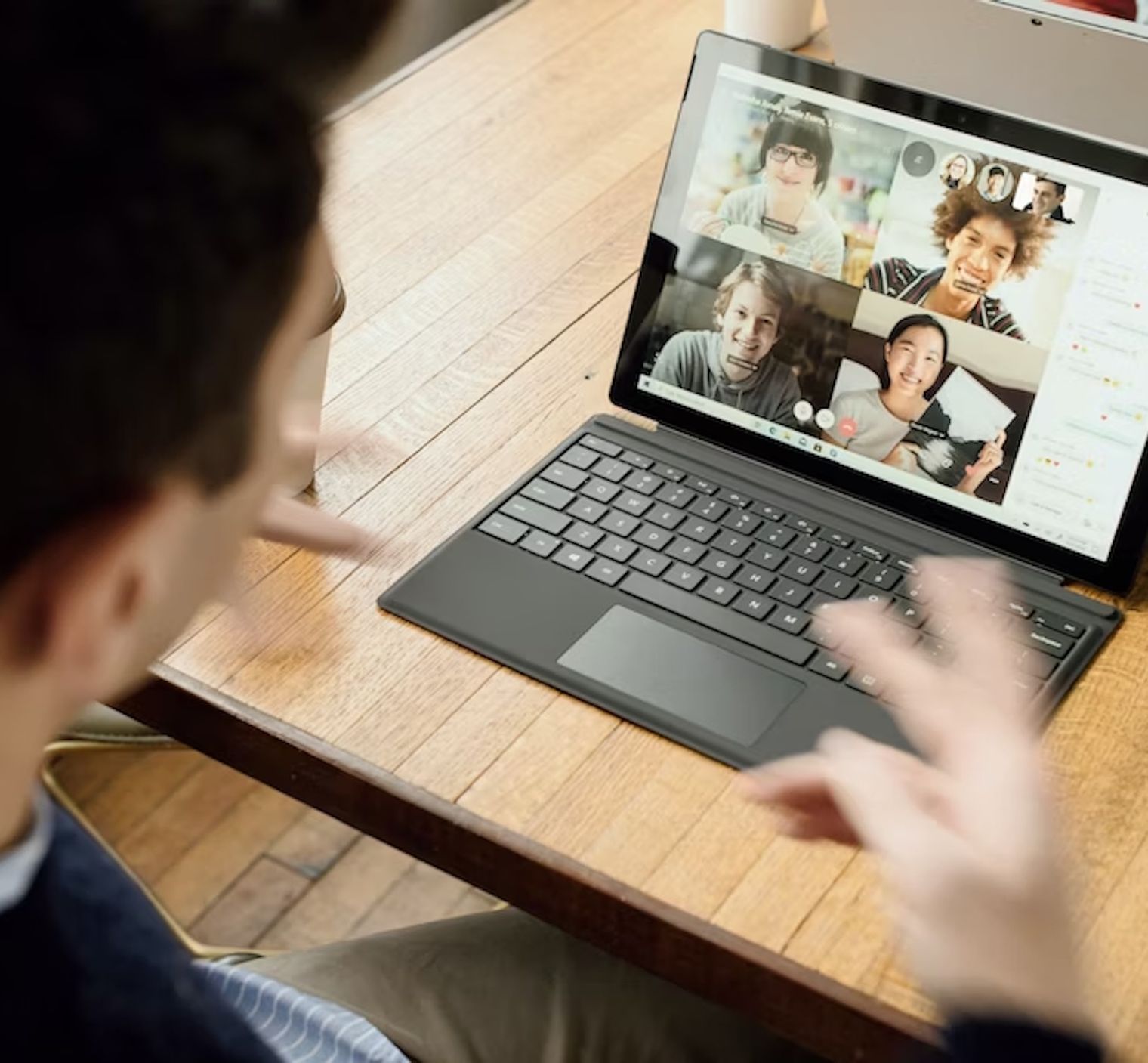

Amidst global shifts, Zoom meetings dominate; but the real magic? Turning those spoken words into accessible text.
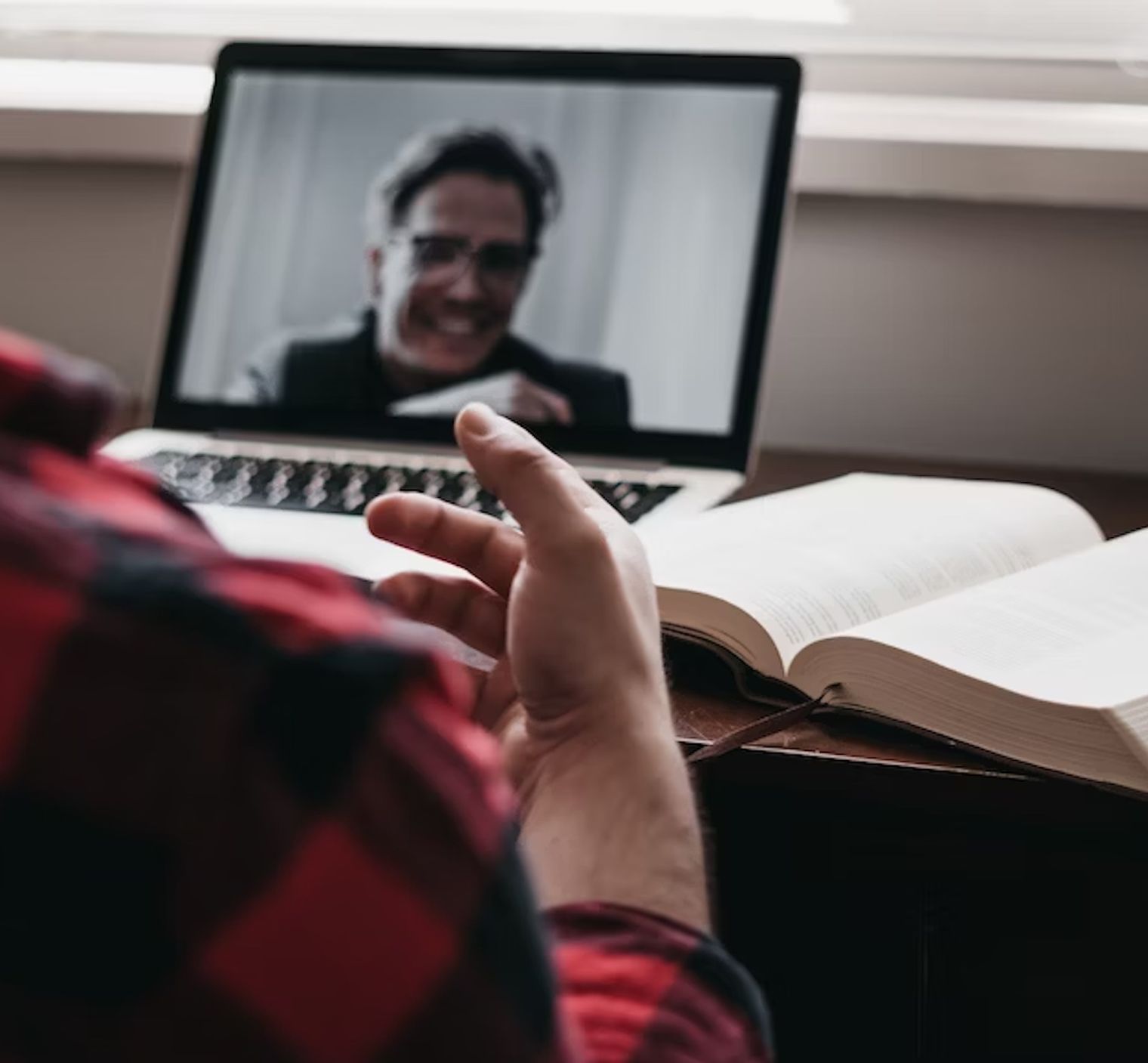

Preserve essential Zoom conversations with accurate, easy-to-use transcription services like Happy Scribe.

Unlock the power of Zoom transcriptions to optimize remote interactions, ensuring every critical detail is captured and easily accessible.

Discover how to effortlessly record, retrieve, and enhance your Zoom meetings, ensuring no valuable discussion goes unnoticed.

Master the art of downloading and preserving your Zoom meetings with this step-by-step guide to optimal recording methods.

Discover how to effortlessly record Zoom meetings on Apple iCloud across various devices, ensuring seamless access and robust security.

In 2020, Zoom's recording feature revolutionized meeting documentation, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
Navigate, manage, and enhance your Zoom recordings with ease through this guide, which also introduces Happy Scribe's transcription services.

Enhance video content with customized subtitles through Happy Scribe, a tool that offers quality and personalized branding for global audiences.

Learn how to enable language interpretation in Zoom meetings using Happy Scribe with this step-by-step guide, enhancing global communication.

This guide provides step-by-step instructions for recording Zoom meetings and webinars without cost, enhancing online collaboration and learning.

Zoom's transcription feature allows easy conversion of video meetings into text, aiding communication in various professional and personal settings.

Understanding Zoom's transcription feature is essential in today's virtual world. This article explains the what, why, and how of Zoom transcription, including third-party service integration.

Explore the intricacies of transcription authorization within Zoom, the role of hosts in meetings and webinars, and how tools like Happy Scribe can enhance virtual communication.

Learn how to integrate Zoom and Google Drive for seamless storage and sharing of video recordings, and discover the benefits of this connection, including Happy Scribe's transcription service.

Navigating Zoom Cloud storage limits is essential for users of this popular video conferencing tool. This article guides you through managing and understanding storage capacity and offers practical solutions.

Zoom recordings serve various purposes, from information retrieval to correspondence. Understanding how to locate, replay, and recover these files, and maximizing their use, can be invaluable.

Zoom Cloud offers users a way to store and manage their virtual meetings securely. This post guides you through accessing, locating, sharing, and transcribing Zoom Cloud recordings.

Explore the features and benefits of Zoom Cloud, including how to record, store, and transcribe meetings, with this comprehensive guide to cloud-based recording on Zoom.

Concerned about Zoom recording expiration? This article guides you on retaining Zoom recordings, accessing expired files, and changing retention settings for both local and cloud storage.

Learn how to export Zoom recordings to your computer, cloud storage, or through third-party tools with this step-by-step guide for sharing and archiving virtual meetings.

This guide offers various methods to convert Zoom files to MP4, ensuring compatibility and ease of sharing, with options for both Windows and Mac.

Learn how to share Zoom recordings through various methods and enhance collaboration, with a step-by-step guide including Happy Scribe services.

Discover methods to record Zoom meetings without host permission and understand the legal considerations and alternatives for capturing content.

Enhance your Zoom meetings with live transcription. It ensures clarity and inclusiveness, even when technical or linguistic barriers arise.

This guide explores the specifics of Vimeo, including memberships, video preparation, file formats, transcription, and subtitles, to help creators optimize their content.

Is downloading Vimeo videos legal? This article explores the legality and methods of downloading content from Vimeo, a leading video platform.

Concerned about missing or deleted videos on Vimeo? This article covers how long videos are stored, deletion reasons, and recovery methods.

Navigating the need for Zoom transcripts? This post offers insights and resources to help you easily record and access transcripts on your PC.

Explore comprehensive steps to send Zoom transcriptions via email, ensuring seamless communication and effective documentation of your meetings and webinars.

Struggling with tracking online meetings or wondering about transcription services? Explore Zoom transcription prices, methods, and how Happy Scribe can be your efficient solution.

Discover how to convert Zoom transcripts into Word documents using automatic transcription tools like Happy Scribe. Enhance efficiency, communication, and record-keeping for your meetings.
Happy Scribe: Your essential tool for transcription and subtitling, empowering media teams to overcome language barriers and connect with global audiences efficiently and effectively."

Wondering how to make a professional video with a minimum effort? Read for some tricks and video editing tips to help you create a great quality video project!

Transcripts, students' best friends, enhance online learning through accurate note-taking, easy archiving, effective studying, and collaborative efforts, revolutionizing education in the digital age.

Increasing eLearning accessibility and efficacy, transcripts are textual representations of course content, aiding student retention, searchability, catering to diverse learning styles and improving SEO.
Learn how to add captions to LMS platforms for enhanced content accessibility, learner comprehension, and inclusivity in E-learning.

Explore the untapped potential of transcription in elevating the effectiveness and inclusivity of today's e-learning landscape.

Select the 'Quiz' option in our 'AI Assist' to automatically create questions for your quiz!

Subtitling boosts social proof, reduces backlash, and enhances accessibility, bolstering online presence. This piece examines its benefits, citing French E-learning platform Skilleos as a case study.

Creating accessible E-learning videos can be a complex task. Happy Scribe simplifies the process by offering transcription, subtitling and customizable features, ensuring an engaging learning experience for everyone.

Subtitling for e-learning improves accessibility and comprehension by providing a text version of audio content. It involves transcribing, timecoding, editing, and formatting captions, syncing them with visual content. This process enhances learning experiences and ensures inclusivity for all learners.

Discover the vital role of captions in e-learning accessibility, and explore the differences between closed and open captions to decide the best fit for your courses. Uncover the significance of popular platforms like Netflix and Google in championing captioning, as well as legal regulations to ensure inclusivity.

In this article, we delve into accessibility challenges within the e-learning industry, and present strategies for creating inclusive online learning environments.

Discover how to enhance accessibility in e-learning by adding subtitles to Loom course videos using the powerful and user-friendly platform, Happy Scribe.

Discover the importance of localizing e-learning courses for global audiences, understanding key elements, steps, and best practices for effective localization.

Explore the benefits of using YouTube for e-learning, understand how to effectively incorporate it into your courses, and learn about the potential of YouTube Shorts for educational content with HappyScribe.

Explore the benefits of including transcripts in e-learning videos, from improved accessibility and comprehension to SEO advantages and legal compliance, and discover effective integration tips.

Discover how Happy Scribe is the ideal alternative for Dotsub’s discontinued transcription and subtitling services in this comparative review.

Discover how Happy Scribe's Make With AI transforms transcripts into professional emails.

This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to maximize the Make With AIBlog post feature, improving blogging capabilities and efficiency.

Explore how Vimeo Library helps manage and share videos, its diverse pricing plans, and integration with Happy Scribe for transcription.

Dive into how subtitles and transcription can boost e-learning accessibility, engagement, and effectiveness for diverse learners.

Here's your quick guide to making e-learning more accessible: learn to create and use SRT or VTT files for video captions

Dive into the world of SRT subtitles on Vimeo, and learn how they boost video engagement, accessibility, and SEO

Master the art of capturing Vimeo videos for offline viewing or improved communication, with this handy guide.

Score more viewers by making your Vimeo videos downloadable, and this guide shows you how to do it.

Dive into this handy guide to learn how to download Vimeo videos in mp4 format for offline use, using both direct and third-party methods.

Explore how Happy Scribe's translation tool can revolutionize your content creation process, making Vimeo live videos more accessible and engaging.

Highlighting the importance of captions and translations, this article provides a detailed guide to video translations on Vimeo for global content accessibility.

Diving deep into Vimeo's free and paid streaming options and their integration with Happy Scribe, we explore benefits and features for content creators.

Master the art of language switching on Vimeo with Happy Scribe to make your videos globally accessible, in 13 easy steps.

Our quick guide to uploading, captioning, and translating your Vimeo videos, manually or with Happy Scribe's help, for a global audience.

Get the lowdown on using Vimeo for live streaming, engaging real-time audiences, and upping your video game with cool features like Happy Scribe subtitles.

Bust language barriers on Vimeo by enhancing your videos with subtitles via Happy Scribe, with this step-by-step guide.

Master the art of making your Vimeo videos globally accessible with subtitles and captions, and don't worry, Happy Scribe's got your back!

Discover how to make the most of Vimeo Record, a versatile tool for screen recording, even when live streaming doesn't fit your schedule

This article provides a step-by-step guide to set up and enjoy live streaming on Vimeo, emphasizing interactivity and viewer engagement.

This article is your go-to guide for converting Vimeo videos into audio files, with reasons why you might want to do it and the best third-party tools to make it happen.

This article provides a comprehensive guide on optimizing your Vimeo video uploads for best quality and experience, highlighting the importance of choosing the right video format.

Live streaming on Vimeo is a breeze: sign up, customize your account, create an event, tweak live settings, and go live!

Experience interactive and high-quality live video streaming with Vimeo Live, offering an easy-to-navigate platform and features for audience engagement.

Explore the diverse range of Vimeo plans catering to personal users, video artists, small businesses, and large corporations

Vimeo, cherished for its high-quality streaming and flexible storage options, offers a comprehensive video-sharing platform with unique features such as customizable branding

The Vimeo Video Library, designed for collaborative workspaces, offers organizations a secure and organized platform to share and manage videos, with features such as automatic transcription

While both YouTube and Vimeo are popular video-sharing platforms, Vimeo provides more comprehensive privacy settings and maintains higher video quality, but YouTube has a larger audience.

Downloading Vimeo videos requires a paid account and, for user-created content, enabling the download option, but third-party options exist.

Vimeo offers an accessible, SEO-enhanced, and high-quality platform for video hosting and sharing.

Vimeo, established by filmmakers and preferred by creative professionals, offers high-quality video hosting and sharing, customizable players, advanced analytics, and integration with transcription services.

Transcribing Vimeo library videos through third-party services like Happy Scribe enhances accessibility, comprehension, data management, and SEO discoverability.

Vimeo offers a transcription service which transcribes spoken language into written text, making videos more accessible

This article discusses the advantages and distinctive features of Vimeo's transcription service, which enhances video accessibility, aids in SEO, and attracts a broader audience.
Learn how to download transcriptions from Vimeo to improve accessibility, SEO, and audience engagement. Follow our step-by-step guide or use tools like HappyScribe to convert and edit files.

This article provides a detailed guide on creating and applying subtitles to Vimeo videos, discussing various subtitle formats supported by Vimeo and the steps to generate subtitles.
Not sure how to add subtitles to a YouTube video? In this article you will find some of the best and easiest ways to add captions to videos.

This article provides guidance on why Vimeo videos may be deleted and outlines the different recovery methods available, whether through Vimeo's platform or utilizing device-level data recovery tools, to assist users in retrieving their lost content.

This article outlines various methods for copying Vimeo videos, whether you're a creator using Vimeo Create or a viewer seeking to download, screen record, or use third-party solutions, all while emphasizing adherence to Vimeo's content sharing rules.

This article provides a comprehensive guide on finding and utilizing English subtitles on Vimeo,

Vimeo offers diverse options for adding subtitles to videos, and when issues arise, such as unsupported formats or incorrect coding, Vimeo provides straightforward troubleshooting steps, ensuring content is accessible and reaches a broad audience.

Vimeo offers various methods for translating videos, including automatic captions, machine translation technology, professional manual translation services, and support for third-party apps like Happy Scribe, ultimately enhancing video accessibility, SEO, and user experience for a global audience.

Improve the accessibility, visibility, and user experience of your Vimeo videos with transcriptions, boosting views and providing clearer messaging.

To transcribe live Zoom meetings without recording, one can use tools like Zoom's Live Transcription and Happy Scribe, each offering unique features like closed captions, easy note-taking, or speaker identification."

Explore how Happy Scribe, an AI-powered transcription tool, can effortlessly convert Zoom recordings into text-based transcripts, benefiting interviews, video subtitles, captions, and academic lectures while offering affordable plans.

Discover how to convert Zoom recordings into text-based transcripts using transcription tools like HappyScribe and Rev.com, allowing easy access, sharing, and reference of meeting contents.

This guide presents the best apps for transcribing Zoom meetings including Happy Scribe, Otter AI, Fireflies AI, Rev, and Colibri, emphasizing their unique features and benefits while highlighting best practices for improved transcription accuracy.

Happy Scribe is a top-tier transcription software lauded for its high accuracy, ease of use, cost-effectiveness, robust features, seamless integrations, outstanding customer support, and user-friendly interface.

This article provides an overview of Zoom's automatic transcription service, the advantages of third-party transcription services.
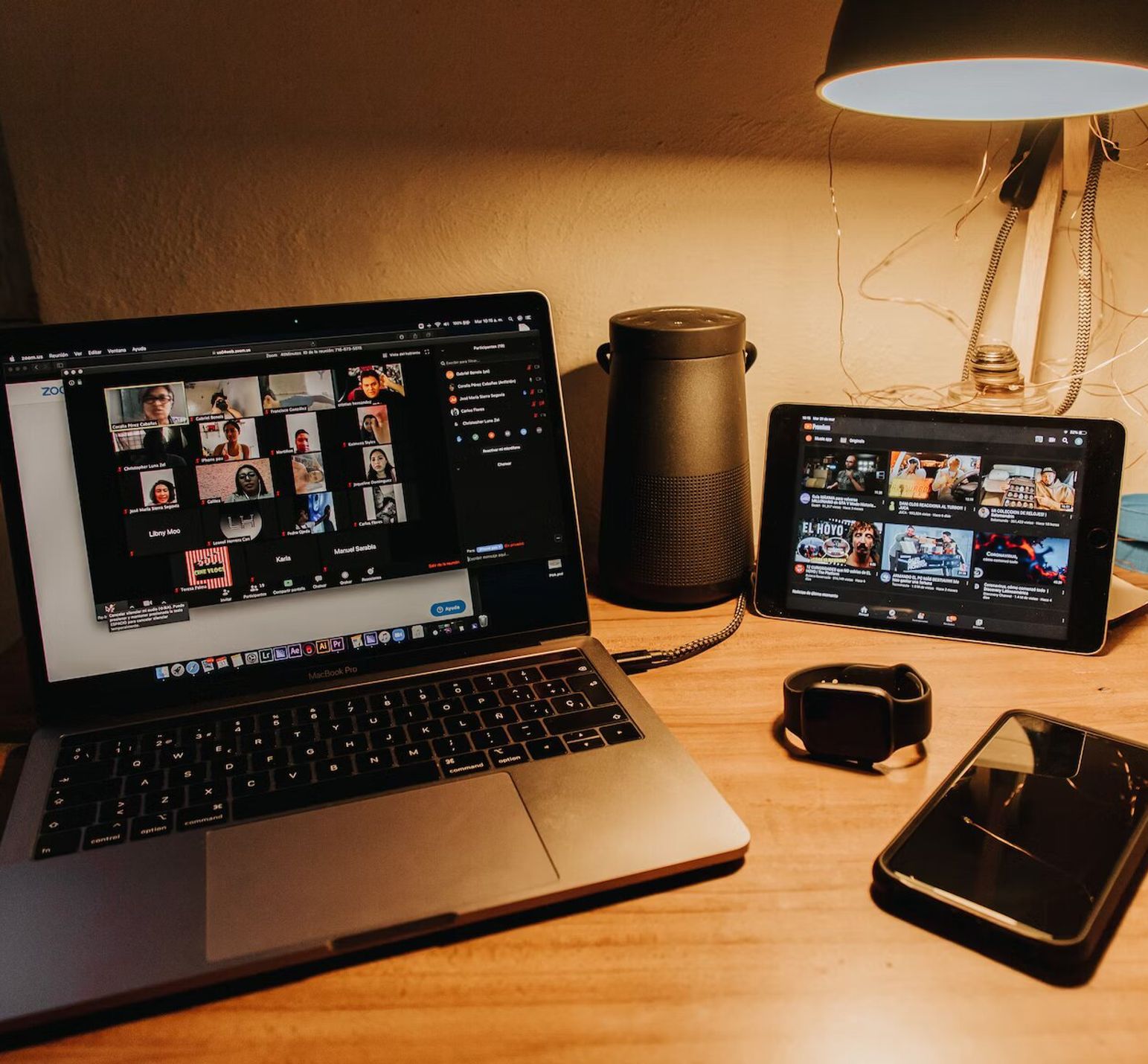

This guide covers how to transcribe Zoom meetings and webinars using Zoom's in-built transcription service and third-party transcription services.
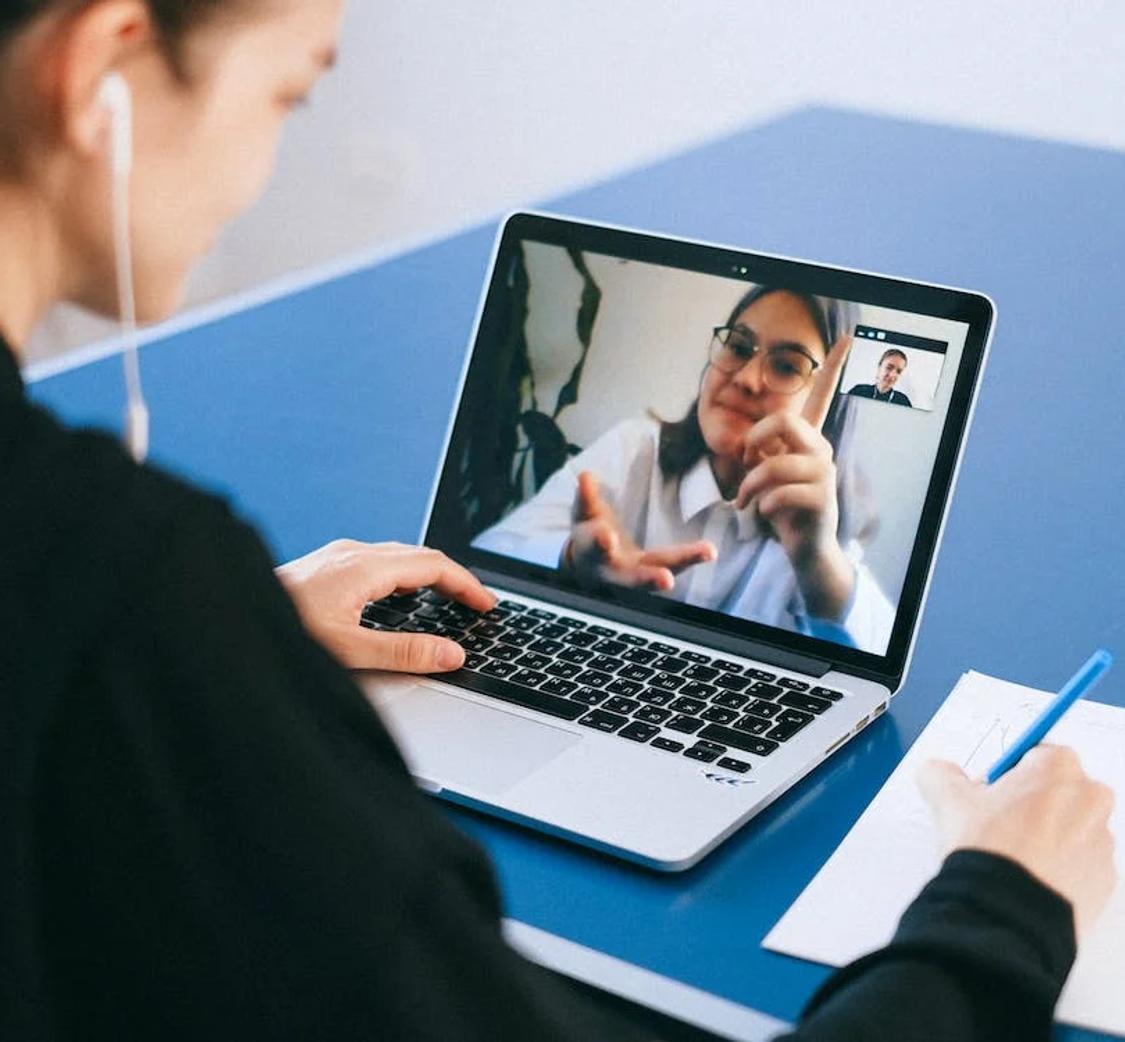

This guide outlines the need for accurate live transcription services during Zoom webinars and presents several options including Zoom's Live Transcription, Otter AI, Colibri, Rev, Verbit, and Happy Scribe, each offering unique features and benefits.

Discover how to simplify the process of navigating through lengthy transcripts by creating chapters with Happy Scribe's AI transcription tool, enhancing readability and productivity across various professions.

This article explains how Happy Scribe's Make With AI tool can make your life easier by automatically summarizing your transcriptions into short, medium, or long summaries, saving you both time and money.

Dive into the differences between SDH and closed captions, and discover how Happy Scribe can revolutionize your video accessibility with automatic, customizable, and multilingual transcriptions.

Discover how to effectively use Vimeo video transcription for interviews. Learn the step-by-step process of transcribing interviews on Vimeo and the benefits it brings.

Discover the benefits of captions, including increased accessibility, broader audience reach, improved attention retention, and easier content navigation.

Learn how to transcribe audio on Vimeo and make your videos more accessible. Explore the steps to obtain video and audio transcriptions using services like Happy Scribe.

Easily enhance your Vimeo video experience by adding subtitles. Learn how to download Vimeo videos and their corresponding subtitle files, and discover different methods for playing videos with subtitles.

Discover how Vimeo video transcription optimizes user experience by improving accessibility, enhancing user understanding, enabling content searchability, and allowing viewers to watch without audio.
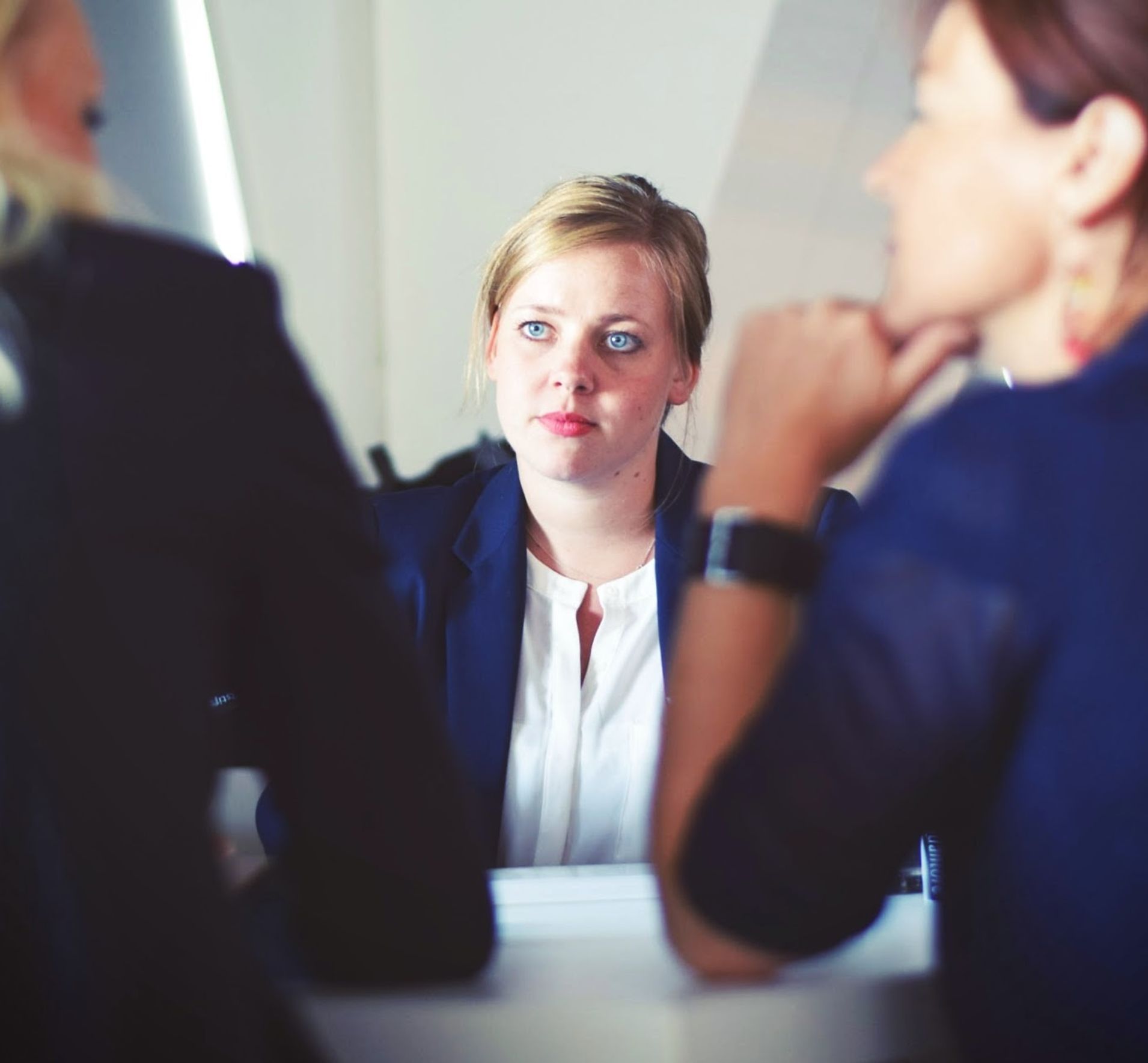

Adding subtitles to videos can increase audience engagement, improve accessibility, and help promote a positive image of a company, making it a useful tool for job postings and promotions.

Transcription platforms automatically convert speech into text files or have human transcriptionists type out the video’s audio to text. We discuss the most important platforms.

Learn how to add subtitles and captions to Vimeo videos in a straightforward and efficient way with this article.

Learn why subtitles don't always appear on Vimeo, how to enable them, and how to add your own captions and subtitles or use third-party software to create transcriptions in different languages.

Third-party transcription tools offer highly accurate transcripts written by human transcriptionists. Users can upload their video transcription files to Vimeo by creating an account with a transcription service, ordering the transcription, downloading it, and uploading it to Vimeo.
Happy Scribe offers fast and accurate closed captioning and translation services for Vimeo videos. Adding subtitles to videos on Vimeo increases accessibility, broadens the audience, and improves viewer engagement

Transcribing Zoom meetings using a third-party application increases engagement, inclusivity, and comprehension while making content searchable and better documented. Third-party transcription apps offer greater accuracy, ease of use, readability, time savings, and extra features like automatic summaries and language support.
Transcription tools efficiently convert Zoom video recordings into Microsoft Word, increasing productivity. Some popular tools offer varying features, supported languages, and pricing. These tools make transcription easier with features like advanced punctuation, speaker recognition, and customizable templates. Choosing the right tool depends on project type, frequency of use, budget, transcript accuracy, and turnaround time.

Transcribe Zoom video recordings for free using tools like Happyscribe. These tools use AI and natural language processing to convert speech to text, enabling easy reference and storage. Factors to consider when selecting a transcription service include accuracy, turnaround time, cost, and compatibility with other platforms. Happyscribe stands out for its features, integrations, and ease of use, making it a top choice for transcribing Zoom recordings.

Zoom Live Transcription offers basic automatic transcriptions, while Happy Scribe provides more accurate, professional results with a free trial. Other tools are available: evaluate options based on your transcription needs and desired accuracy.

Transcription tools for Zoom meetings and webinars vary in price and accuracy, depending on whether they are machine-generated or human-generated. Machine-generated transcripts have an 80-85% accuracy rate and cost around $0.25 per audio minute, with monthly plans ranging from $8-$30. Human-generated transcripts boast a 99% accuracy rate but cost around $1.50-$3 per minute.
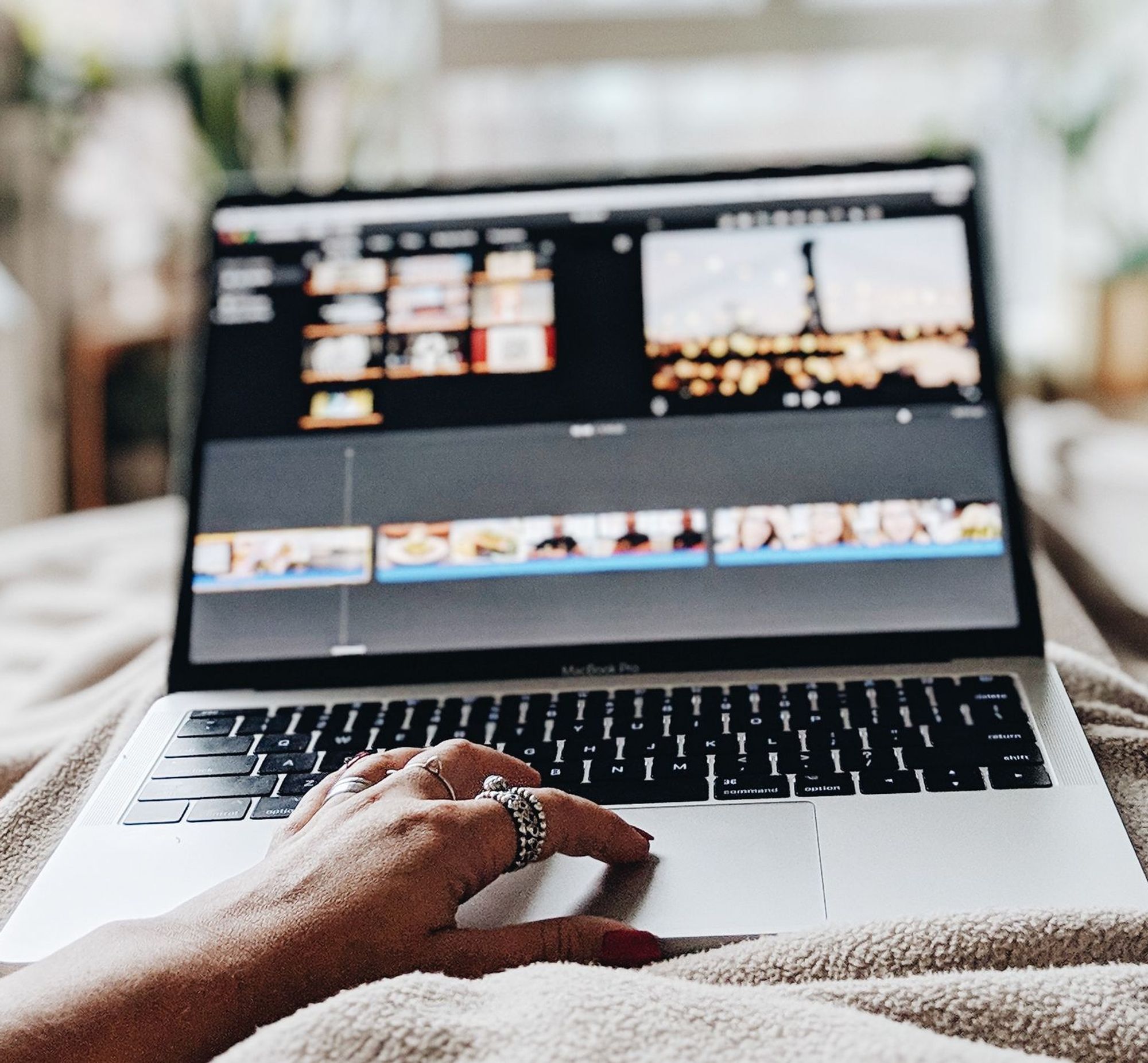

Use Happy Scribe to get a free SRT file for your 30-minute video.

Looking for the best captioning software of 2026? We tested the top AI and human transcription tools for accuracy, speed, and price. See why HappyScribe is our #1 pick.
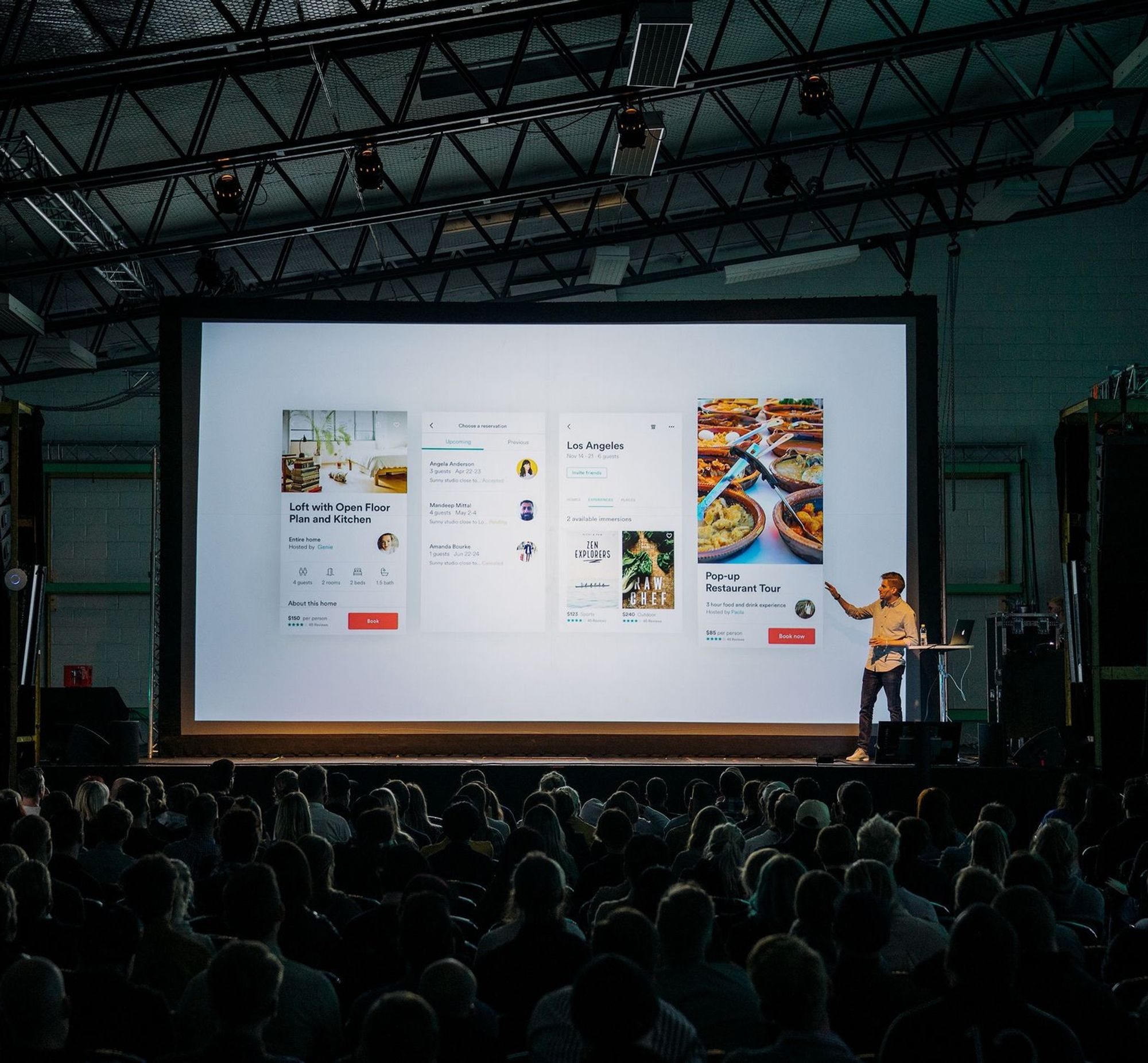

Audio to text and video to text transcriptions of conference speeches offer many versatile ways to improve your conference.

Your subtitles need to be readable and perfectly synced with the video and perfectly follow the reading skills of your audience. For example, you don't make subtitles for adults the same as subtitles for children.

Creating a money-generating eBook from your existing podcast episodes shouldn’t take too long. Just follow these six simple steps.

What are the pros and cons of recording and note-taking? Which one is right for you?

In this post we analyse the best ai transcription software you can use in 2026 to auto generate transcripts. Compare the best tools for transcription available in the market.

Seven practical solutions audio and video creators can implement to make web content more accessible for the Deaf and hard of hearing.

Getting insightful data from any focus group begins with meticulous pre-planning. Start by asking these five essential questions.

Did you ever wonder if they were an iPhone application that was able to record and transcribe the audio into text at the same time?

Increasing your GPA is easy when you record and transcribe your lectures. Here is how audio to text technology can help you.

How do you get a quality audio recording on your smartphone? Follow these simple steps. Better audio means a more accurate automatic transcription.

How do you get accurate subtitles and captions on your Facebook page videos? It is actually easier than you think. Here is an easy step-by-step guide to follow.
Transcribing your Instagram stories is great way to improve your SEO and maintain strong Google Search rankings for your videos. Instagram stories are one of the most popular features of Instagram, but most aren’t accessible to deaf and hard of hearing people. So what to do? How do you

Creating a WebVTT subtitle file is lightening fast with Happy Scribe's Subtitle Generator. This tutorial shows you how.

There are two easy ways to convert audio cassette tapes to a digital format such as MP3. Happy Scribe shows you how.

Creating minutes of a meeting doesn't have to be time-consuming. Use an automatic transcription service provider to get meeting minutes accurately and quickly.

Staff burn-out and high costs by trying to manually transcribe over 1500 radio broadcasts stored in the Library and Archives Department. As a result of using Happy Scribe’s services, Biola University was able to reduce their costs by 80%.

Follow these simples steps to get the most from recording and automatically transcribing your academic lecture.

Use Happy Scribe's handy checklist to see if your video is accessible.

Six criteria to consider when choosing which transcription method is best: manual, automated transcription service provider, or human-based.

Thinking of creating a how-to video Follow these six steps to create the perfect how-to video and you will increase your viewership and boost your SEO in no time.

LINC (Leadership for INCLusion in the Early Years) is an higher education level programme which enables practising early years’ educators to support the inclusion of children with additional needs in their early years of education. LINC has grown to be Ireland’s largest blended learning cohort in higher education offering

Have you ever wondered, 'What is the difference between transcription and translation?' If so, read on.

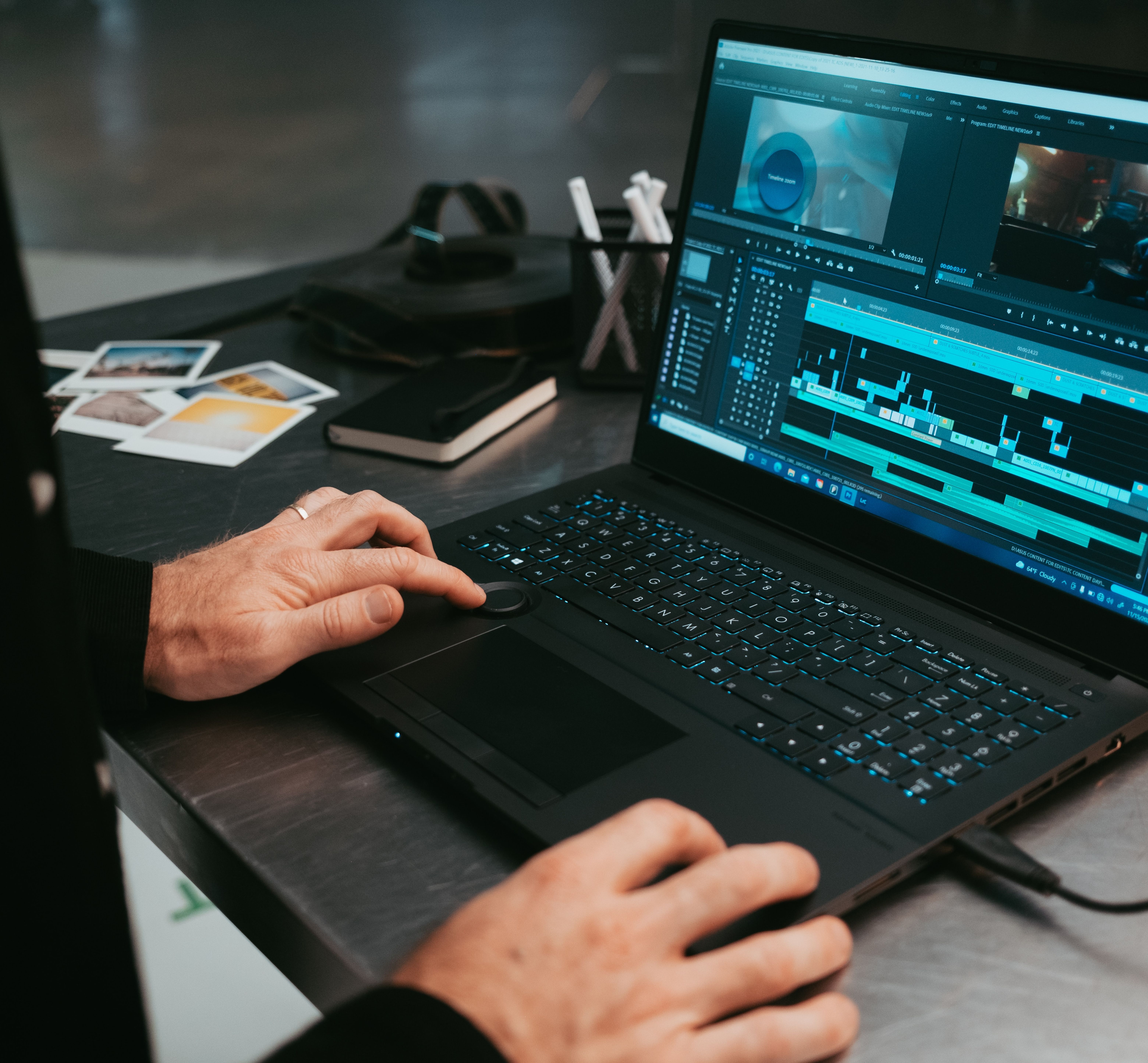
Being efficient and saving time is the key to success for any video editor. Use these 5 productivity hacks to help you stay focused, work faster, edit smarter and stream-line your post-production approach.
Our Embed Player is out of service

Whether you are a professor who records oral histories for your research or a market researcher looking to document the conversations that took place during your most recent focus group, Happy Scribe’s transcription services allow us to easily transcribe your audio files to text in just a few minutes.

Adding subtitles to your Youtube video is a great move if you want to increase your viewership and make your content more accessible for deaf and hard of hearing. By default Youtube does not display closed captions. In this tutorial, we will show you step by step what to do

These tips will provide you a better quality audio recording, which will in turn increase your audio-to-text transcription accuracy.

Crafting quality show notes has many benefits, but creating them doesn't have to be time-consuming. We show you the benefits and how automatic transcription can speed up the process.

Learn how to record and transcribe a Google Hangouts Meet video in any language: French, Spanish, German, Arabic, Italian or +114 other languages and accents.

Have you ever received a WhatsApp voice message that you would rather read? Here we explain how you convert a WhatsApp audio to text. And we explain why voice messages are becoming popular again.
Are you a video editor transcribing video audio to text? Make sure you are avoiding these these common mistakes.

There is a quick and cost-effective way to ensure that online courses are accessible to all: add captions to Blackboard videos. Happy Scribe shows you how.

Including transcripts with e-Learning videos helps improve the overall learning experience for both learners and teachers. Here's how.

High-quality recordings are essential to transform an interview into a high-quality transcription. To achieve crystal clear sound quality invest in this essential equipment.

We’ve reviewed dozens of productivity tools on the market and provide you with our list of the most essential productivity tools for podcasters.

Adding subtitles to your LinkedIn video posts is a simple process. Happy Scribe shows you how.

Voice recognition is the ability of a machine or program to identify words and phrases in spoken language and convert them to a machine-readable format. Designing a machine that mimics human behavior, especially the capability of speaking and responding to it, has intrigued engineers and scientists for centuries. Speech technologies

There is nothing quite like enjoying a good film, series or documentary, and really getting immersed in the story. But what happens when that great piece of art is not in a language you can understand? And what happens when you can see the video but physically can’t hear the audio? That’s where subtitles and closed captions (CC) come in. Both bits of timed on-screen text offer language access and language accessibility, supporting a full viewing experience, but they do so in different ways. In this article we are going to explain how.

Using YouTube's automatic captioning service is tempting: it's free. However, there are some serious limitations to consider.

SDH subtitles ensure that video content can be accessed by the entire Internet population. Happy Scribe discusses their attributes and why you should use them.

These tips and techniques will help ensure that you conduct a professional interview and help you get meaningful information and useable quotes.

If you’re one of the many freelance writers that makes up the ‘gig economy’, you’re in good company. Latest figures suggest that there’s 2 million freelancers in the UK, most of whom work in professional and technical occupations – namely writing. As self-employment has grown, so has the

Conference rooms around the world are now in darkness, with many businesses relying on virtual meetings to stay connected. Follow these tips to host, record and transcribe a successful virtual meeting.

Five important software tools for podcasters.
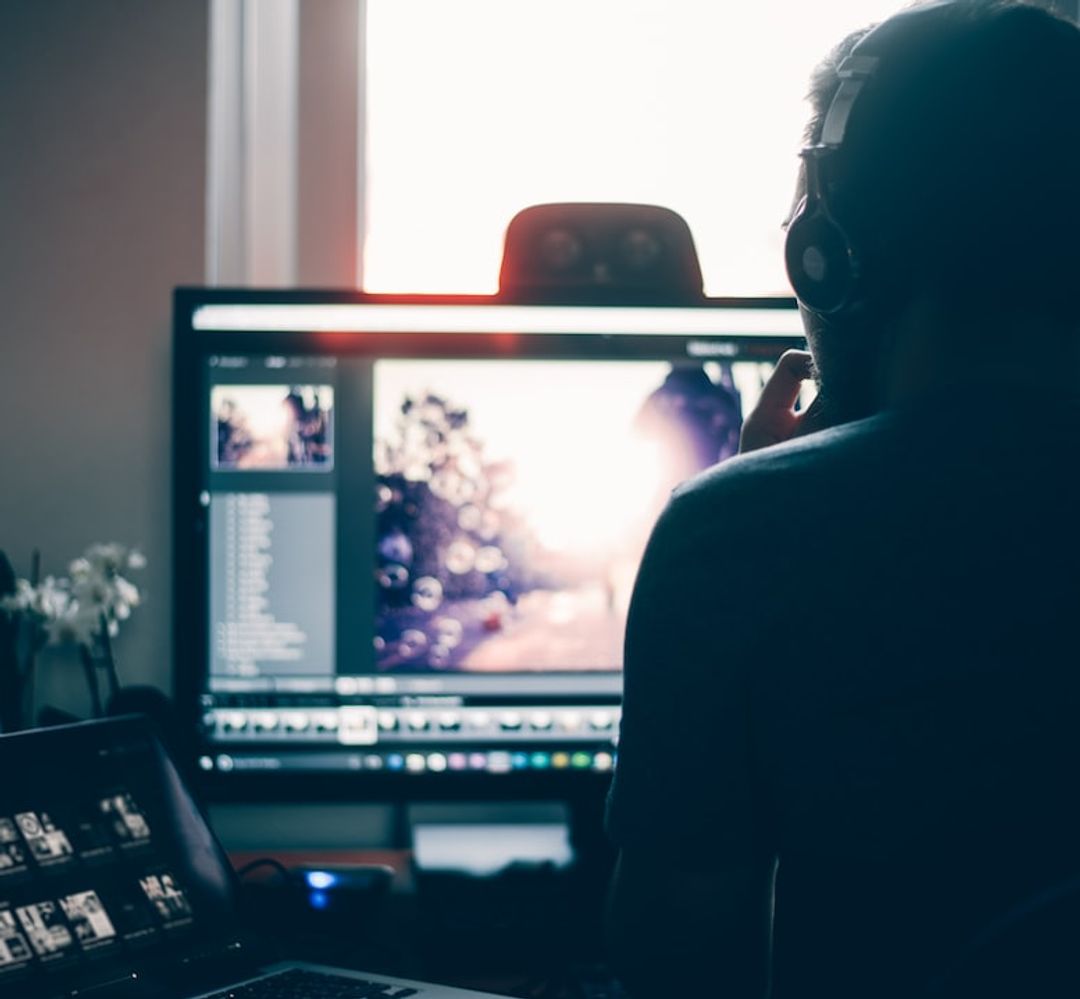

For documentary producers, it can be very important to create markers to fast-track the editing process. Postproduction and production companies can use Happy Scribe to fast-track their projects. Creating transcripts is making the post-editing process much more efficient. However, when you have dozens if not hundreds of recording hour to

Two weeks ago we question ourselves on what happy scribers were doing with the transcripts ordered on Happy Scribe. We saw that the final purpose of most transcriptions was to have a basis to collaborate with peers. So, here we are, today, we are releasing Happy Scribe for Teams.Teams

An SRT file allows video editors to insert subtitles or closed captions. Learn how to easily create a custom SRT file.
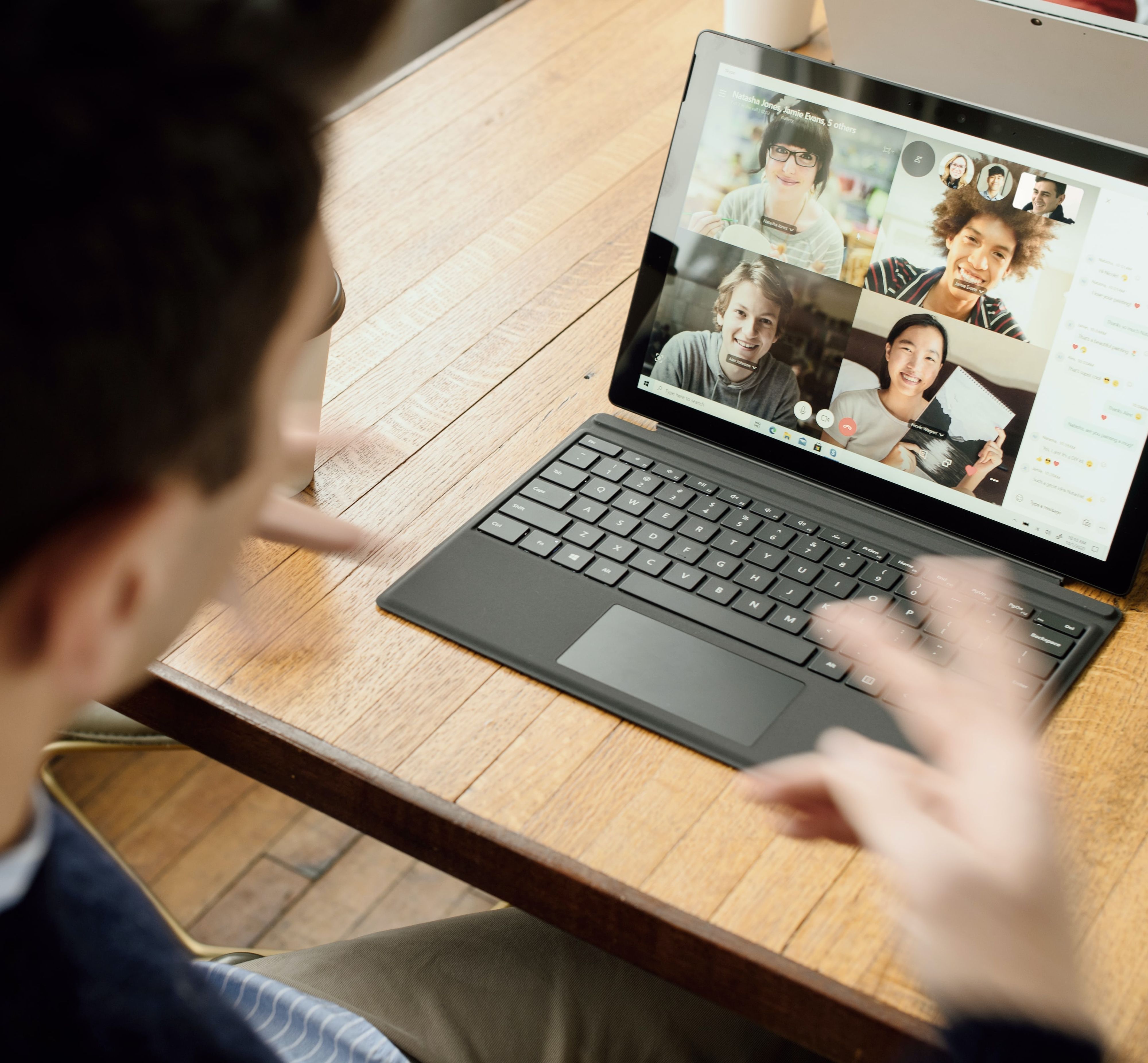

Video calls and meetings are essential in the business world, but language barriers can be a challenge. Zoom's transcription service helps bridge the language gap, supporting a variety of languages for live transcription. While the accuracy of Zoom's captions is generally high, it lacks a dictionary tool, leading to occasional errors with names, acronyms, and content-specific terms. Additionally, Zoom's supported languages are limited to 22, which may not cover all users' needs.