How To Transcribe a WhatsApp Audio to Text

I have a confusion. I hate voice messages. I absolutely loathe them. I find them intrusive, cumbersome, annoying and down right arrogant of the sender.
But it appears, I’m becoming more alone in this thought. Maybe it’s my age, but recent research indicates that a bizarre phenomenon started to occur in the middle of 2018. Mobile users started ditching texts in droves in favour of voice messages.
Say what?!
Whilst text messages, have dominated the way we have communicated to each other for the last decade, 2018 saw a shift towards more voice chats. In fact, the British newspaper The Sun stated that roughly 200 million voice messages are sent over WhatsApp every single day! Whilst in Asia, mobile users on WeChat, the Chinese equivalent of WhatsApp, sent 6.1 billion voice chats last year. And even FaceBook reports that voice memos are the second most popular form of file sharing through its Messenger platform, just after photos.
Are you in as shock as me? Or are you one of these early adaptors that have already ditched text in favour of the old school voice message?
Do you want to know why this ridiculous craze is coming back in vogue?
Do you realise that sometimes, you need the text version of these voice chats and want to know how to convert them?
If you need answers to any of these questions, then read on.
Why Are We Seeing Growth in Voice Messages Again?
I can understand the attractiveness of the voice message over text for a sender. With a voice message, there is no fumbling your fingers over a tiny keyboard and no having to correct typos. Your hands are free to sip your coffee. Or you can leave a message as you are walking down the street without worrying about falling off the curb and twisting your ankle. And let’s face it. Sending a voice message is a ton faster, particularly if you have a lot to say.
But, this has always been the case with voice messages, so why the sudden resurgence of such an annoying technical device now?
Based on my extensive research, it seems the increased use of voice messages is due to these three key factors: increased international communication, a desire for more human connection, and the rise of home assistant devices.
WhatsApp (and other messaging apps like WeChat) are becoming a common space for international communication in an increasingly global world. However, toggling between language keyboards to find the right characters for a language can be exhausting. Or in the case of Chinese text, painfully time-consuming. Additionally, lots of cheaper Android phones (predominate in developing countries) have weaknesses in the way that they are able to type a local language. Therefore sending a voice message is just quicker and easier.
Another reason is the increased desire for human connection. There is a growing backlash to the digital age, which has left us more discounted from individuals than ever. Leaving a voice message is more intimate. You can hear the laughter in someone’s voice. You can detect if a message is flirtatious. You can feel the warmth. Text messages don’t offer that. Voice messages are just more nuanced and your emotional meaning comes across easier and eliminates the laborious task of hunting down the perfect gif or emoji to accompany your text message.
Finally, the rise of home assistants is making it more natural for people to talk to a device to get something done. Consider today’s youth who are growing up with the likes of Alexa in their homes. They are accustomed to asking a machine to play their favourite music or to turn on their lights. Asking them to convert back to using a small keyboard to send a text message seems alien to them. The result is that today’s 15 to 25 year olds accept voice messaging as a more natural behaviour.
How does a Voice Message Impact the Receiver?
Whilst the voice message may be ideal for the sender’s needs, it doesn’t take the context in which the person on the other end might receive it. Maybe you are hearing impaired and find it difficult to listen to a voice message. Maybe you don’t have your headphones handy and are in a public place where you don’t want your private messages to be overheard. Or maybe you are on a boring conference call, where you can’t actually play a distracting voice message.
There is no doubt about it, in these instances scanning a text would be more preferable.
Frankly, for the receiver, voice messages are seen as a bit of a hassle. Beyond the situations where it’s not convenient to listen to a message and the annoyance of having to dig out your headphones, there are also some practical instances where reading a text message would be better.
Consider this example: Your boss owes you some specific information you need for an important client meeting you have later in the day. Your boss could have sent you a brief email, but they are on their morning commute to work and decide to get a jump start on the day by sending you several 45 second voice messages instead. You, on the other end, now must listen to the messages and try to take notes to get all the exact detail. There is no pause or rewind, and because the message is in your second language, you have to stop and rewind and listen all the way through again. Several times. A process that ends up taking you a frustrating 20 to 30 minutes.
ARGH!
How do you convert a voice message to text quickly?
If you are in one of these situations, then fear not. Happy Scribe can help.
Our online application can quickly convert audio-to-text in the blink of an eye. Well a few minutes actually, but if the message is important and you need to read all the detail then getting a transcription is vital.
Here’s what you need to do to convert that annoying WhatsApp audio to text:
- Open your WhatsApp message and hold your finger over the voice message you need to convert to text.
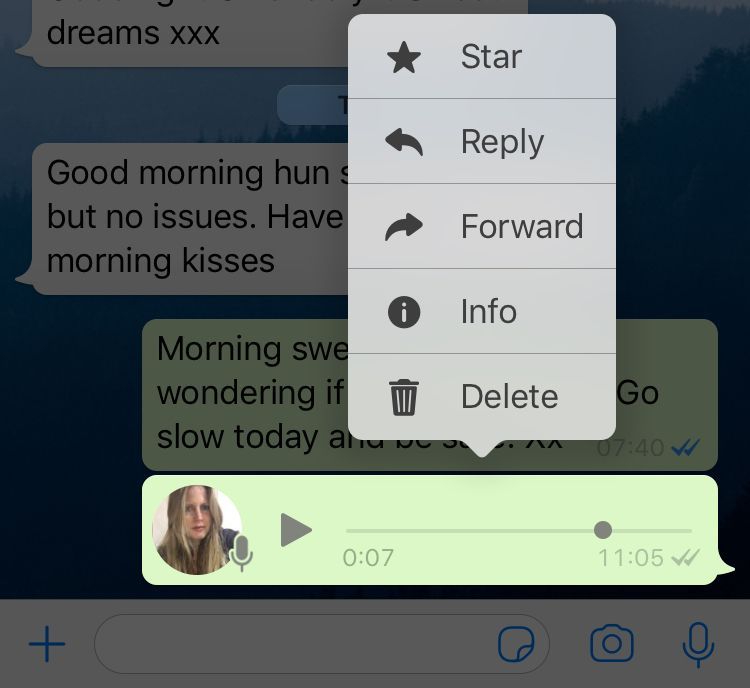
2. A list of options will pop up. Click forward.
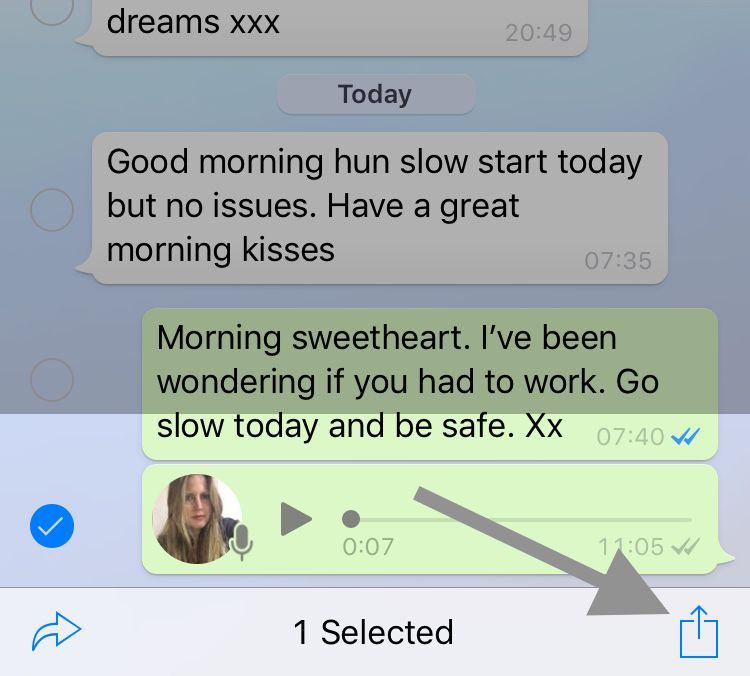
3. Check the message or messages you want. Then click on the right hand box with the arrow. Finally click Save To Files
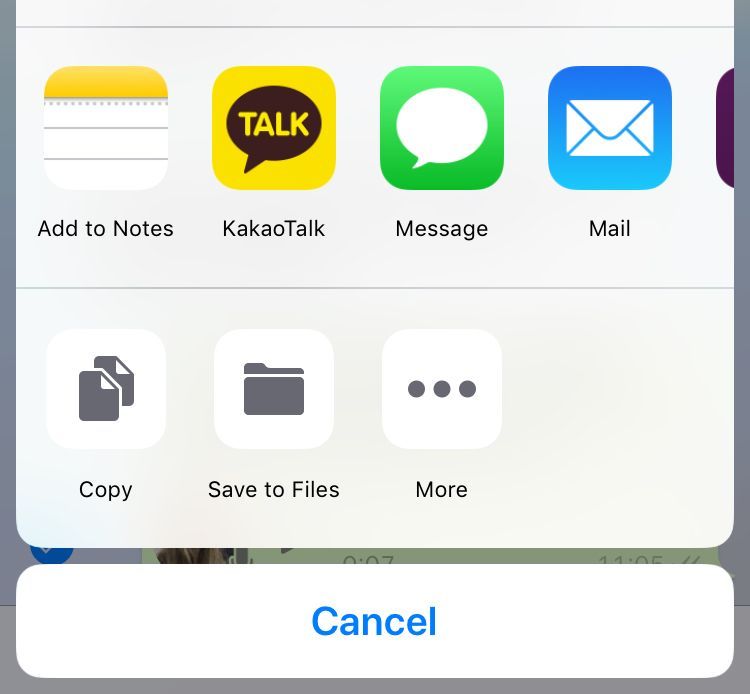
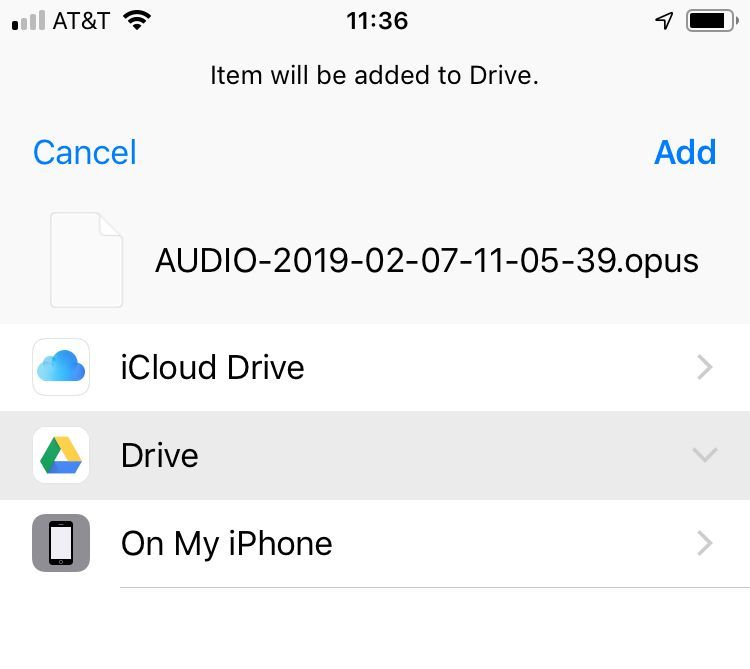
4. Click on Drive/Add
5. Next, Go to Happy Scribe
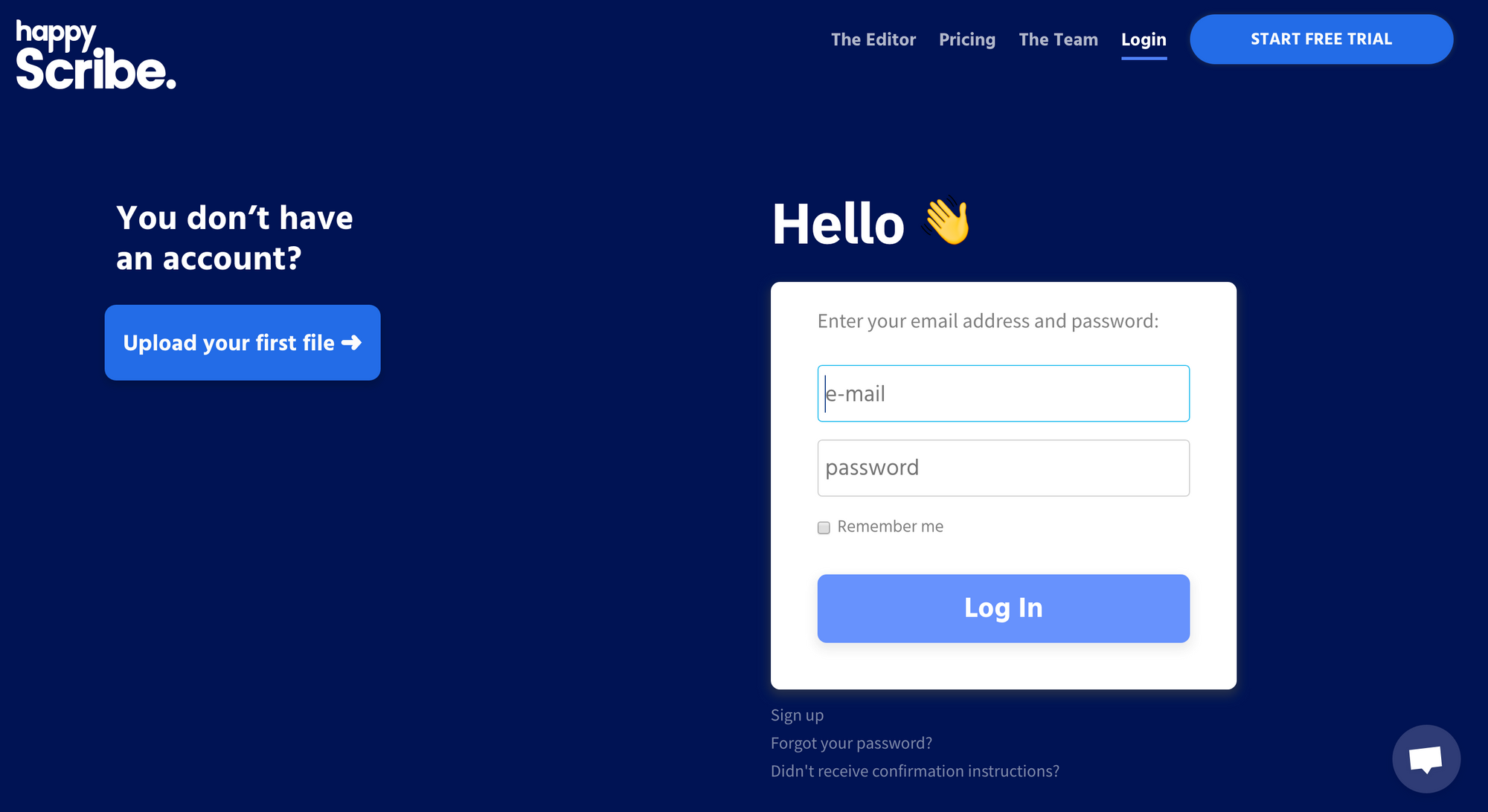
6. Create an Account or Login
7. Go to where you saved your file - in this case in Google Drive. Upload your file.
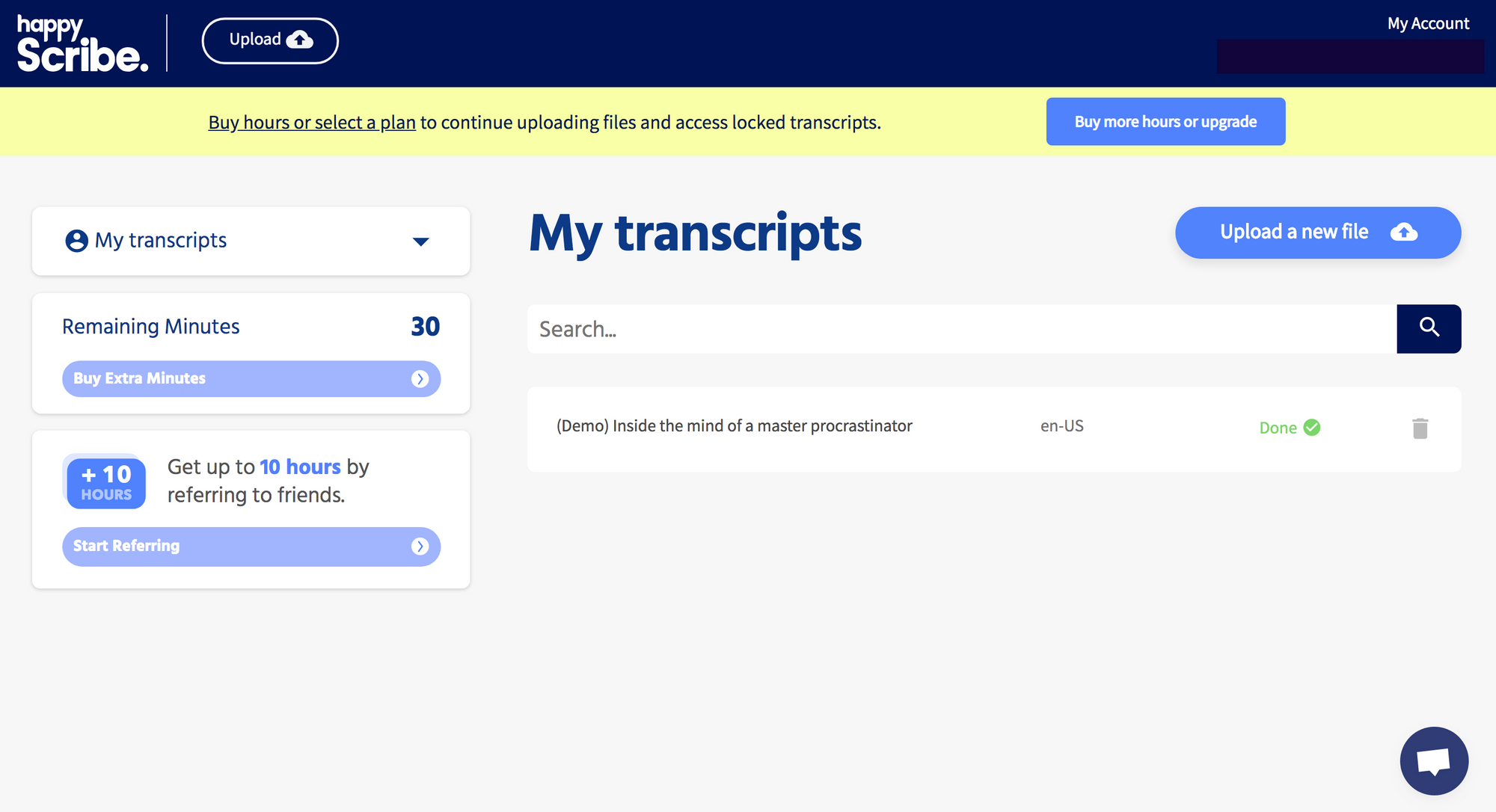
8. In a minute, your voice message will be converted to text. (You can sip your coffee, send some emails or take a quick nap whilst this is happening in the background.)
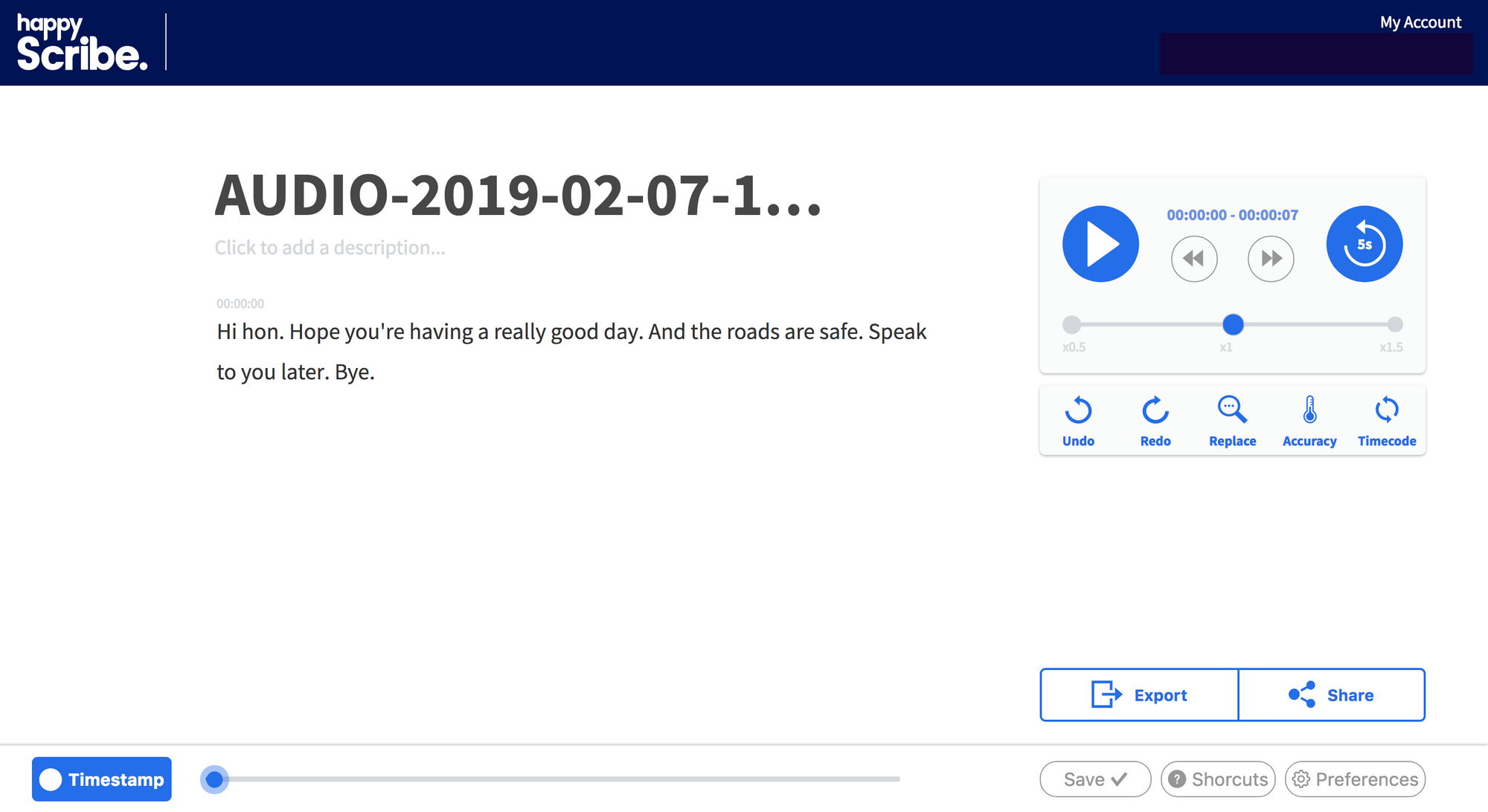
I appreciate that this may not be the ideal solution for those short 15 second clips, but for longer messages - like the ones from your boss that are full of detailed information - then this is the way to go.
And longer voice messages are increasing. Djamal Agaoua, CEO of Viper (a messaging app), noted in a recent podcast with The Verge’s Ashley Carman that they recently extended the maximum length of voice messages to 15 minutes and saw a huge uptick of usage in the function.
I can assure you that if anyone sent me a 15 minute voice message, it would never get listened to, but if I could convert it to text, then yeah, I might read it and answer you back.
If we can help you with transcribing your WhatsApp voice messages, then get in touch.
Explore our guide to transcribing Korean
Explore our guide to transcribing Korean
Explore our guide to transcribing Korean
Explore our guide to transcribing zulu

André Bastié
Hello! I'm André Bastié, the passionate CEO of HappyScribe, a leading transcription service provider that has revolutionized the way people access and interact with audio and video content. My commitment to developing innovative technology and user-friendly solutions has made HappyScribe a trusted partner for transcription and subtitling needs.
With extensive experience in the field, I've dedicated myself to creating a platform that is accurate, efficient, and accessible for a wide range of users. By incorporating artificial intelligence and natural language processing, I've developed a platform that delivers exceptional transcription accuracy while remaining cost-effective and time-efficient.